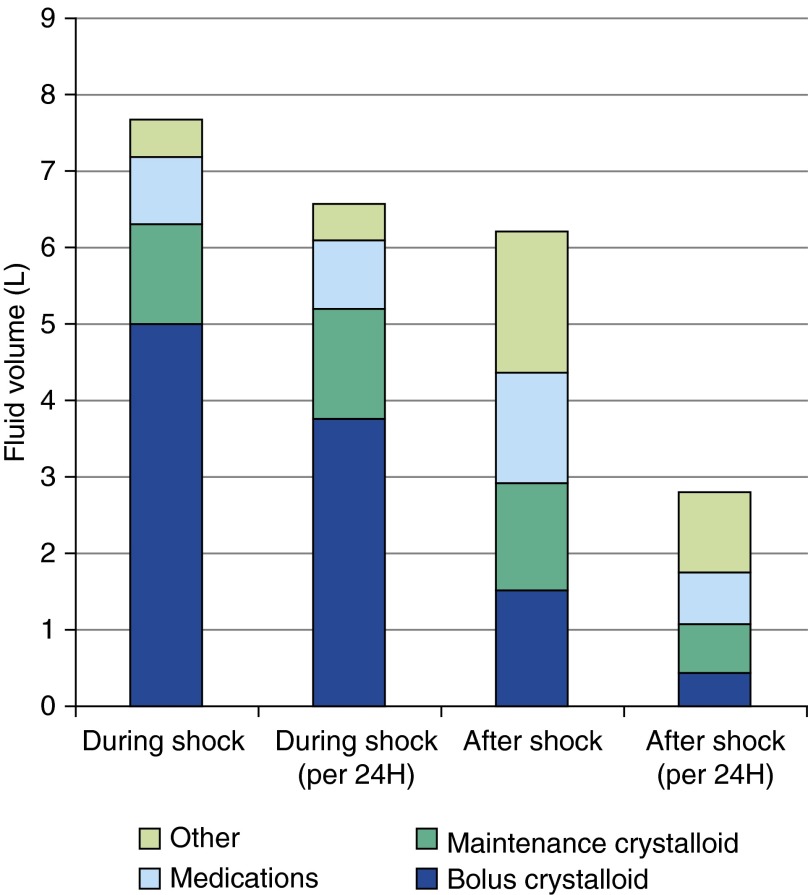
Figure 2.
Fluids administered during shock and after shock resolution. Shock resolution was defined as the end of 12 hours in the intensive care unit without vasopressors and without more than one mean arterial pressure reading less than 60 mm Hg. Volumes presented are the median for each fluid category. “Other” fluid consists of albumin, blood, total parenteral nutrition, enteral nutrition, free water, and oral fluids. Crystalloid includes dextrose 10% in water, dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer solution, dextrose 5% in water, dextrose 5% in water with 0.45% NaCl, dextrose 5% with 0.45% NaCl-KCl 20 mEq/L, dextrose 5% with 0.45% NaCl-KCl 40 mEq/L, dextrose 5% with 0.9% NaCl, lactated Ringer solution, and sodium chloride 0.9%. Maintenance crystalloid was composed of any of these fluids given at a rate less than 250 milliliters per hour, and bolus crystalloid was any of these fluids given at a rate of 250 milliliters or more per hour.