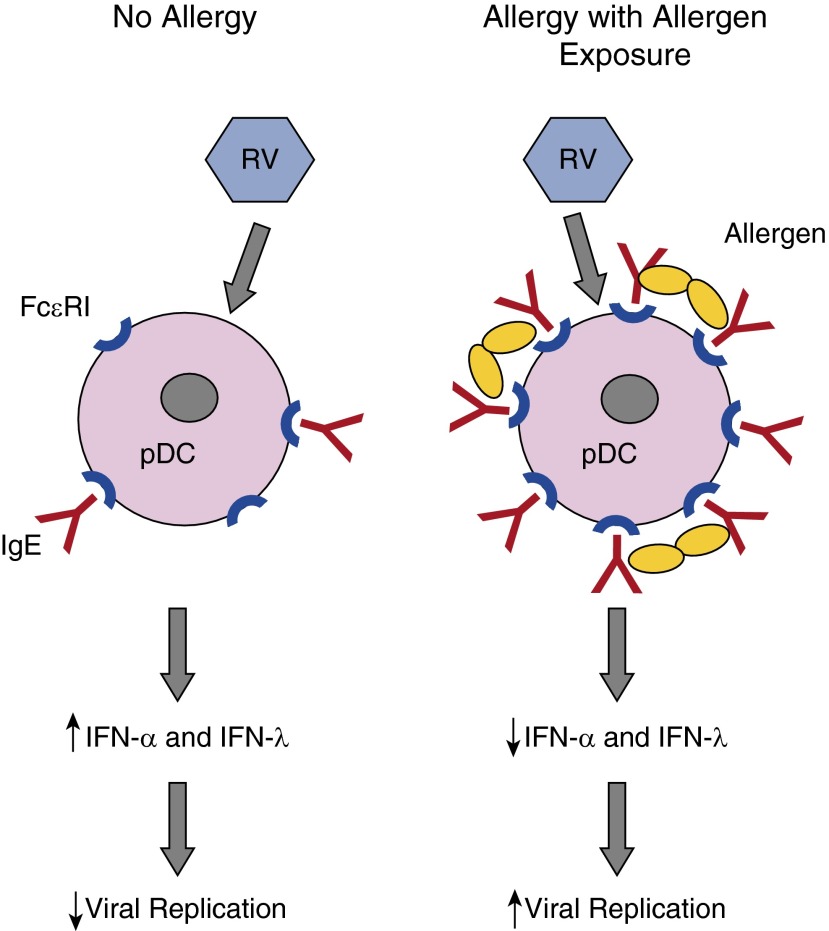
Figure 1.
High-affinity IgE receptors (FcεRIs) on plasmacytoid dendritic cells and effects on interferon responses. In the absence of allergy, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) express low levels of cell surface FcεRI, and some of these receptors are occupied by IgE. Rhinovirus (RV) infection induces pDCs to secrete IFN-α and IFN-λ, which inhibit viral replication in an autologous and paracrine fashion. In the context of allergy with allergen exposure, FcεRI and IgE are increased, and cross-linking of receptors by allergen can inhibit interferon secretion. The net result in asthma could be increased viral replication, more severe illness, and increased risk for exacerbation of chronic asthma. Figure courtesy of William W. Busse, M.D., University of Wisconsin-Madison.