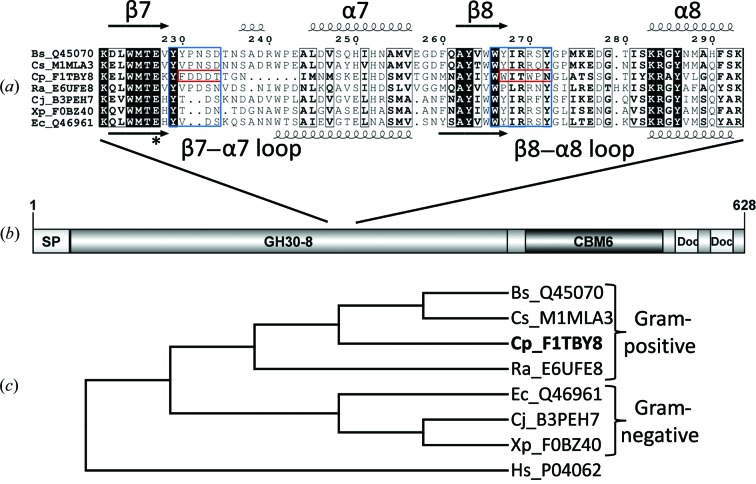
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis of CpXyn30A. (a) An alignment with conserved secondary-structure elements of the β7–α7 and β8–α8 loop regions representing the area of GA coordination in the characterized GH30-8 enzymes (BsXynC, Bs_Q45070; EcXynA, Ec_Q46961). The specific regions which contain the amino acids which directly coordinate the GA are boxed in blue and the same regions from CpXyn30A are in red. (b) The domain architecture of CpXyn30A showing the GH30 catalytic module followed by a family 6 CBM and two dockerin domains presumably for inclusion in a cellulosome complex. (c) Phylogram depicting the distribution of CpXyn30A relative to homologous GH30-8 Gram-positive and Gram-negative derived enzymes rooted to a GH30-1 enzyme. Sequences are identified through their unique UniProt accession number preceded by the initials of the bacterium. Other sequences used in this comparison included Cs_M1MAL3 from C. saccharoperbutylacetonicum, Ra_E6UFE8 from Ruminococcus albus, Cj_B3PEH7 from Cellvibrio japonicus, Xp_F0BZ40 from Xanthomonas perforans and the GH30-1 subfamily enzyme Hs_P04062 from Homo sapiens used as an outgroup for the phylogenetic analysis.