Fig. 5.
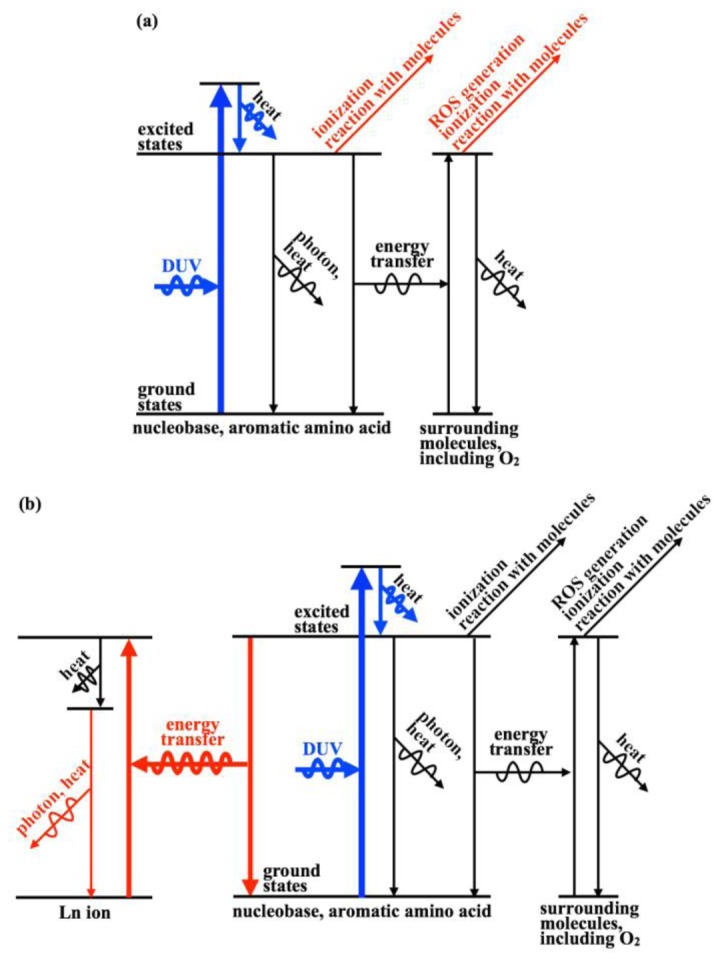
Energy pathways of nucleobases and aromatic amino acids in a cell under DUV (λ = 257 nm) exposure. Regardless of the type of Ln ion, nucleobases or aromatic amino acids are excited by absorbing DUV light, then is immediately relaxed to the vibrational ground state of the electronic excited state having the lowest energy. (a) Without Ln ion, the excitation of nucleobase or aromatic amino acid is followed by ionization, reaction with molecules, and relaxation to the electronic ground state. The relaxation pathways are thermal and radiative decays or energy transfer to surrounding molecules. The energy transfer to surrounding molecule is followed by ROS generation, ionization, reaction with molecules, and thermal decay. (b) With Ln ion, FRET from the excited nucleobase and aromatic amino acid to the higher energy level of Ln ion can occur. Ln ion is relaxed to the lower excited energy states by heat emission and further relaxed by thermal or radiative decays.
