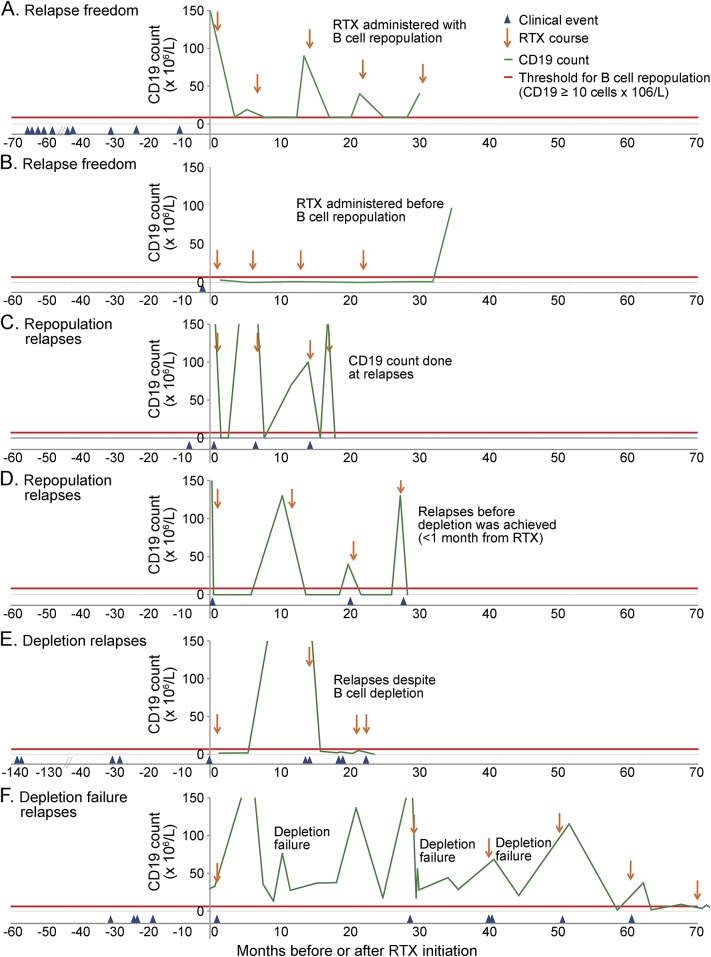
Figure 3. Summary figure exemplifying 4 different types of response to rituximab treatment observed in our patients.
Relapse freedom with rituximab (RTX) (A, B), occurrence of relapses with a repopulated B cell count (“repopulation” relapses; C, D), occurrence of relapses with a depleted B cell count (“depletion” relapses; E), occurrence of relapses in association with failure to reach B cell depletion (“depletion failure” relapses; F). (A) Relapse freedom (no relapses during rituximab): rituximab redosing after B cell repopulation (patient 14). (B) Relapse freedom (no relapses during rituximab): rituximab redosing before B cell repopulation (patient 10). (C) “Repopulation” relapses (relapses with B cell repopulation): repopulation was detected only at the time of the relapse (third and fourth relapses); subsequent rituximab courses were administered after the relapse (second and third rituximab courses) (patient 4). (D) “Repopulation” relapses (relapses with B cell repopulation): repopulation was noticed at CD19 count monitoring and rituximab was administered, but clinical relapse occurred a few days after rituximab, before depletion was achieved (second and third relapses) (patient 5). (E) “Depletion” relapses (relapses despite B cell depletion in the last 3 relapses) (patient 2). (F). “Depletion failure” relapses (relapses associated with failure to reach B cell depletion in the first, second, and third rituximab courses). In this patient, B cell depletion was achieved in subsequent rituximab courses (total 9 courses; same rituximab regimen used in all the courses, 1,000 mg × 2). The figure shows only the first 5 courses; no relapses occurred subsequently.