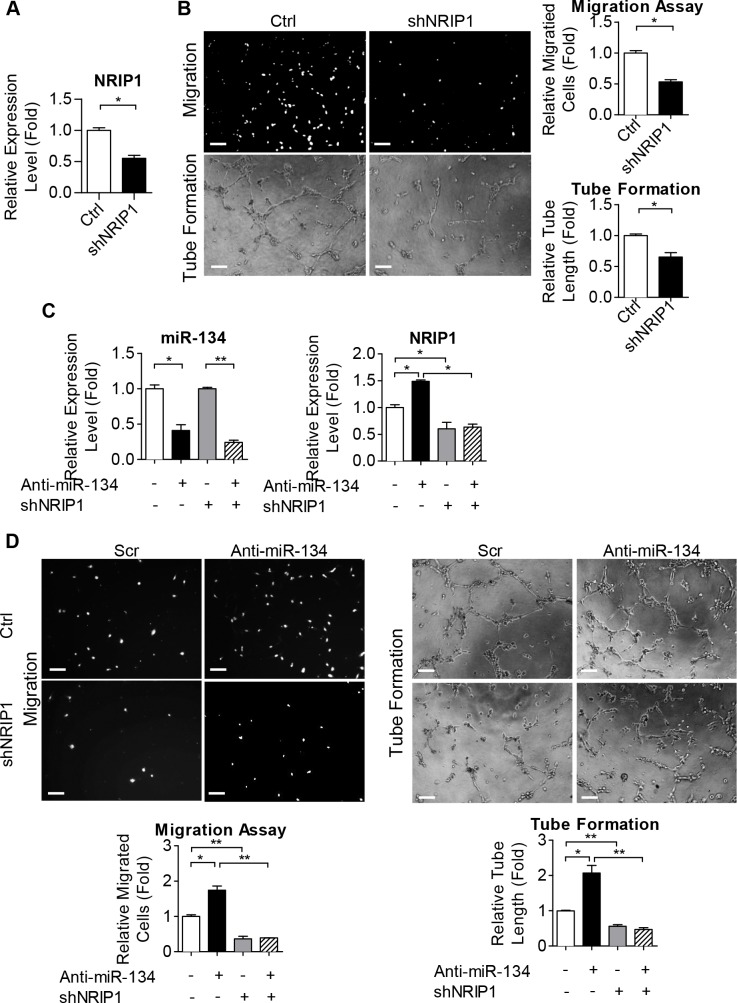
Fig 6. NRIP1 is involved in ECFC activity and is crucial for miR-134 functionality.
(A) Validation of NRIP1 in dfECFCs infected with NRIP1 shRNA. * p < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test. (B) Representative images (left) and quantitative data (right) from the Transwell migration assays (upper) and microvascular formation assays (lower) using ECFCs infected with control or NRIP1 shRNA plasmids. n = 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) The expression levels of miR-134 and NRIP1 in dfECFCs treated with miR-134 antagomir and NRIP1 shRNA as a double manipulation. n = 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. (D) Representative images (upper) and quantitative data (lower) of the Transwell cell migration assays (left) and tube formation assays (right) using dfECFCs with miR-134 antagomir and NRIP1 shRNA as a double manipulation. n = 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. Scale bar: 50 μm. Ctrl: plasmid control, shNRIP1: NRIP1 shRNA, Anti-miR-134: miR-134 antagomir.