Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used for treatment of sepsis in China, but results still remain equivocal. To evaluate the safety and efficacy of TCM for sepsis, we conducted this Meta-analysis. Methods: Databases searched included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (up to December 2014). The studies included used routine therapy treating sepsis in the control group and TCM was added on that basis in the experimental group. Methodological quality was assessed by Cochrane criteria for risk of bias. Results: Ten RCTs with 691 participants were identified and analyzed. In the meta-analysis, TCM plus routine therapy reduced the 28-day mortality compared to routine therapy alone, [RR = 0.67; 95% CI: 0.51~0.87; P = 0.002]; The decrease in length of ICU-stay [MD = -1.82; 95% CI: -2.60~-1.04; P<0.00001]; Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation system (APACHE II) score [MD = -2.95; 95% CI: -3.99~-1.91; P<0.00001]; Serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment [SMD = -0.50; 95% CI:-0.68~-0.33; P<0.00001], including TNF-α [SMD = -0.61; 95% CI: -0.85~-0.38; P<0.00001] and IL-6 [SMD = -0.40; 95% CI: -0.75~-0.04; P = 0.03] in subgroup analysis all had statistical significance. Conclusion: Addition of TCM has better effects in participants with sepsis, while more high-quality studies are needed to draw firm conclusion.
Keywords: Traditional Chinese medicine, sepsis, meta-analysis
Introduction
Sepsis is a systemic, deleterious host response to infection or injury leading to severe sepsis and septic shock, which is believed to be the major cause of death in ICUs [1,2]. An epidemiologic study claimed an incidence of 37% for sepsis and 30% for severe sepsis in European ICUs [3], and the 1-year all-cause mortality of participants with severe sepsis and septic shock may be as high as 44% [4]. The pathogenetic mechanism and physiologic changes are exceedingly complex, according to the pathogenesis of sepsis, in addition to the damage of pathogenic microorganisms and the toxin, disorder of the immune function also plays a key role in the development of sepsis. Pathogenic factors like infection ,toxin and so on, produce a variety of cytokines in participants with sepsis, in which the most significant are TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-10 [5]. These inflammatory mediators cause serious consequences in the body, like, inflammation of endothelial cell, the dysfunction of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis, abnormal vascular tone and myocardial depression, etc. Nowadays, despite of the great progress in anti-infective therapy and the support of the organ function, mortality of severe sepsis is still up to 30%~70% [6].
Routine therapies including support of organ function and administration of intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and oxygen is still nonspecific, limited [7]. Given the importance of inflammatory response in sepsis, new approaches targeting the host immune response may be efficacious in reaching a better outcome. Traditional Chinese medicines (TCM), for example, astragalus membranaceus, salvia miltiorrhiza, angelica sinensis, chuanxiong, have been found to have anti-inflammatory or immune modulation effects and help to regulate and improve the immune function [8]. Some mechanisms have been disclosed, which will discussed later. Researches [9-18] included in this mata-analysis using Chinese medicine as a part of treatment for sepsis showed that the treatment can improve the physical condition and prognosis of participants with sepsis.
To our knowledge, no quantitative analysis has been done for combination of related data. Therefore, in the present review, we evaluated findings from recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the efficacy and safety of TCM for sepsis to determine whether it is beneficial to participants with sepsis.
Methods
Search strategy
We searched the electronic libraries including PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (up to December 2014) to make sure that the articles included might be provided with higher quality. All databases were searched without language limitation. Potentially relevant trials included the terms “traditional Chinese medicine” or “Chinese herbal medicine” or “Chinese traditional medicine”, “sepsis” or “pyaemia”, and “randomized control trial”. We retrieved the full texts to assess the studies for inclusion. Only data available in the full text were reviewed.
Inclusion and Exclusion criteria
Studies had to satisfy all the following criteria for inclusion into the review: (1) trail: randomized controlled trials (RCTs); (2) participants: adults and diagnosed as sepsis; (3) interventions: TCM plus routine therapy versus the same routine therapy alone, or TCM alone versus routine therapy; (4) outcome: appropriate and normative outcome measures, relevant data should be available in the full text. Studies were excluded if they conformed the following criteria: (1) trail: non-randomized controlled trials (NRCTs), animal experiments, review articles; (2) participants: children or participants with other diseases; (3) interventions: TCM plus routine therapy versus the thired treatment; (4) outcome: outcome measures were not appropriate, relevant data could not be obtained from the original author. (5) duplicated publications. The eligibility of included studies was assessed by two reviewers independently. Any disagreement was solved by discussion between the two reviewers, and finding a third reviewer for judgment if necessary.
Outcome measurements and data extraction
Two reviewers (L.X. and Z.M.) independently extracted the main outcome data to evaluate the difference between the experimental group (TCM plus routine therapy) and control group (routine therapy). The outcome measurements are as follows: (i) Primary outcomes: 28-day mortality; (ii) Secondary outcomes: length of ICU stay, APACHEⅡ score after treatment, the concentration of serum inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-6) after treatment. And extraction forms (Tables 1, 2) were specially made for baseline assessment. Items in the forms included (1) characteristics of the studies (author, year of publication, country of study, journal, type of the study); (2) participants (sample size, age and gender, APACHE II score, infectious status); (3) interventions (experimental and control group, duration of treatment, route of TCM); (4) outcome.
Table 1.
Characteristics of included RCTs (part A)
| Study | Gender | Age | APACHE II score | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TCM+RT | RT | TCM+RT | RT | TCM+RT | RT | Infectious status (number of patients) | Duration of treatment | Route of TCM | |||
|
|
|||||||||||
| male | female | male | female | ||||||||
| Huang RL [9] (2014) | 13 | 7 | 12 | 8 | 54.7±14.9 | 55.7±17.3 | 18.3±3.8 | 20.1±4.3 | Not mentioned | 7 days | nasogastric tube/oral |
| Shao M [10] (2011) | 21 | 18 | 12 | 13 | 55.7±15.3 | 56.2±15.5 | 14.6±6.2 | 15.9±6.9 | intra-abdominal infection (19), pulmonary infection (23), CNS infection (11), intrauterine infection (3), skin and soft tissue infection (4), urinary system infection (2) | 7 days | intravenous drip |
| Su YL [11] (2008) | 59 | 23 | 58 | 27 | 69.48±15.15 | 69.41±16.20 | 16.70±8.09 | 16.78±6.83 | Not mentioned | 10 days | nasogastric tube/oral |
| Wang B [12] (2011) | 22 | 10 | 21 | 11 | 57.6±8.3 | 63.1±7.9 | 18.21±5.97 | 17.87±6.26 | pulmonary infection (54), peritonitis (6), biliary tract infection (5), intracranial infection (2), multiple infection (16) | 9 days | nasogastric tube/oral |
| Zhang CH [13] (2011) | 15 | 7 | 15 | 8 | 58.4±16.3 | 60.1±18.6 | 21.6±5.4 | 22.4±5.2 | Not mentioned | 7 days | nasogastric tube/oral |
| Wang CX [14] (2011) | 14 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 59.88±10.25 | 59.50±11.85 | 24.73±2.57 | 25.27±3.24 | pulmonary infection (12), peritonitis (2), trauma (2), cholecystitis (3), severe pancreatitis (3), hepatapostema (3), viral encephalitis (1) | 3 days | nasogastric tube |
| Jiang RL [15] (2009) | 9 | 18 | 18 | 7 | 65.4±12.1 | 68.8±12.9 | 20.1±3.8 | 19.2±3.5 | pulmonary infection (34), severe pancreatitis (3), intestinal fistula and peritonitis (8), biliary tract infection (4), blood stream infections (3) | 5 days | intravenous drip |
| Qiu ZL [16] (2012) | 20 | 16 | 18 | 14 | 49.3±15.5 | 50.5±17.2 | 17.58±5.77 | 18.28±5.66 | Not mentioned | 7 days | intravenous drip |
| Zhang SL [17] (2010) | 9 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 60.9±17.5 | 58.7±16.8 | 11.6±6.0 | 11.4±6.2 | peritonitis (14), biliary tract infection (11), severe pancreatitis (13), septic shock (12) | Not mentioned | nasogastric tube/oral/rectal |
| Gao ZL [18] (2012) | 25 | 20 | 21 | 19 | 61.70±11.64 | 60.36±14.62 | 22.89±7.47 | 21.95±9.33 | Not mentioned | 7 days | intravenous drip |
Table 2.
Characteristics of included RCTs (part B)
| Study | Type of study | Interventions (control group) | Interventions (experimental group) | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang RL [9] (2014) | RCT | routine therapy (refered to 2008 SSCa guidelines) | routine therapy; Sini Decoction (ripe aconite root, dried ginger, honey-fried licorice root) | ACTH stimulating test; 28-day mortality; APACHE II score; 3-day shock recovery rate |
| Shao M [10] (2011) | RCT | routine therapy (refered to 2004 SSCa guidelines, bundle theraphy) | routine therapy; Xuebijing injection (extractive of safflower, red peony root, rhizoma chuanxiong, salvia, angelica) | Expression rate of Th17 and CD4+ CD25+Treg; 28-day mortality; ICU stay; APACHE II score; |
| Su YL [11] (2008) | RCT | routine therapy (refered to 2004 SSCa guidelines) | routine therapy; Qishen huoxue granule (astragalus membranaceus, salvia miltiorrhiza, flos carthami, angelica sinensis, chuanxiong, etc.) | 28-day mortality; ICU stay; Marshall score; APACHE II score; Serum inflammatory factors concentration |
| Wang B [12] (2011) | RCT | routine therapyb | routine therapy; Modified Liang-Ge San (fructus forsythiae, scutellaria baicalensis, gardenia, lophatherum gracile, rheum officinale, mint, mirabilite, liquorice, radix scrophulariae, salvia miltiorrhiza, radix ophiopogonis, American ginseng) | Platelet parameters/activation; platelet TLR4 expression; intensity of inflammatory response; rate of bleeding; 28-day mortality; ICU stay; APACHE II score; TNF-α concentration |
| Zhang CH [13] (2011) | RCT | routine therapyb | routine therapy; Hengyan medicinal recipe (bombyx batryticatus, periostracum cicada, turmeric, rheum officinale, astragalus membranaceus, radix ophiopogonis, red ginseng, cortex moutan, peach seed, flos carthami, etc.) | Number of bowel movement; levels of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ T cell; APACHE II score; Serum inflammatory factors concentration |
| Wang CX [14] (2011) | RCT | routine therapy (fluid resuscitation) | routine therapy; Modified Qianyang Pellet (fructus amomi, monkshood, tortoise plastron, rhizoma zingiberis, ephedra, honey-fried licorice root) | Extravascular lung wate parametersr; oxygenation index; 28-day mortality; |
| Jiang RL [15] (2009) | RCT | routine therapy (refered to 2004 SSCa guidelines) | routine therapy; Shenfu injection (extractive of red ginseng and black Fupian) | DO2, VO2, ERO2, lactate clearance rate; 28-day mortality |
| Qiu ZL [16] (2012) | RCT | routine therapy (refered to 2008 SSCa guidelines) | routine therapy; Shenfu injection (red ginseng, extractive of black Fupian) | 28-day mortality; Marshall score; APACHE II score; Serum inflammatory factors concentration |
| Zhang SL [17] (2010) | RCT | routine therapyb | routine therapy; Fufang qingxia Decoction (rheum officinale, magnolia obavata, immature bitter orange, mirabilite, fructus forsythiae, dandelion, double blossom, gardenia, Cortex Moutan) | TNF-αconcentration; expression of TNF-α mRNA |
| Gao ZL [18] (2012) | RCT | routine therapy (anti-infection, nutrition support, glucose control with insulin pump) | routine therapy; Shenmai injection (extractive of red ginseng and ophiopogon), sulfotanshinone sodium injection (extractive of Salviae Miltiorrhizae) | serum levels of CRP, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6; the HLA-DR expression of the peripheral monocytes; 28-day mortality; APACHE II score |
SSC: Surviving Sepsis Campaign;
no description about routine therapy in the study.
Quality assessment
The methodological quality was assessed according to the guidelines recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration [19] by two reviewers (G.X.Y. and L.C.B.) independently. Six categories (randomization and sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding method, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting, and other sources of bias, the first three considered as “key domains”) were evaluated, each one summarized into three levels: low risk, unclear risk, and high risk. The risk of bias of a particular study was assessed according to the levels of the three key domains: LOW (low risk of bias for all key domains); UNCLEAR (unclear risk of bias for one or more key domains); and HIGH (high risk of bias for one or more key domains).
Statistical method
We used Review Manager (RevMan®) (Version 5.1.; The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK) and Stata® (Version 10.0.; Stata Corp, College Station, TX, USA) to analysis the data. Included studies were categorized according to the outcome measurements. Dichotomous data were calculated as the relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Continuous data were calculated as mean difference (MD) with 95% CI, standardized mean difference (SMD) would be used if the data were of great difference or had different measurement units. Heterogeneity was evaluated by the I2 value. P>0.05 or I2<50% meant low risk heterogeneity, and a fixed-effect model would be used; P<0.05 or I2>50% meant high risk, the source of heterogeneity would be analyzed and a random-effect model would be used if the heterogeneity was unclear. We would just give a description of the results if the data took on obvious heterogeneity. Begg’s Test was carried out to access the potential publication bias. P<0.05 was considered as the statistically significant value.
Results
Study selection
As was shown in Figure 1, a total of 114 studies were searched. After reviewing the abstracts, 88 studies were excluded because of not meeting the inclusion criteria, nine potential duplications were found and discarded. We obtained 17 studies for detail evaluation. Seven studies were excluded for no related data. The remaining ten non-duplicated RCTs that compared TCM plus routine therapy (RT) with RT alone were included.
Figure 1.
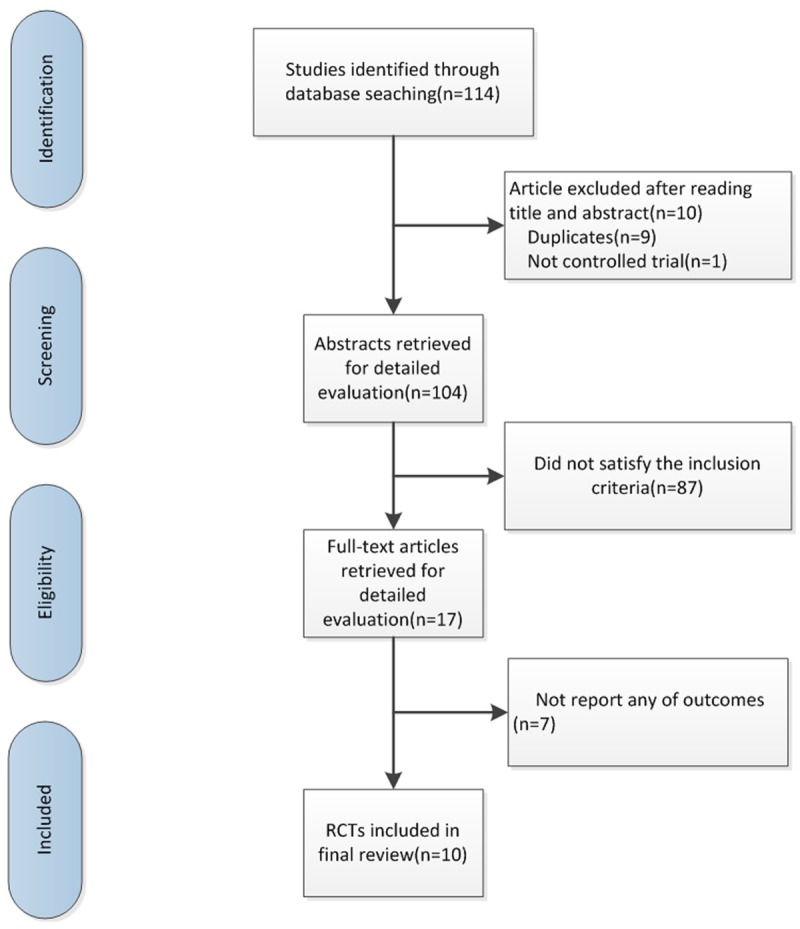
Search flow diagram for studies included in the meta-analysis. RCTs, randomized controlled trials.
Study characteristics and quality assessment
All included ten studies were single center RCTs conducted in China, involving 691 participants. All the studies were similar at baseline and low quality researches. The Cochrane risk of bias was presented in Figure 2. Eight studies [9,11-16,18] described the random method, while two of the studies [14,18] were not completely random. Only one study [9] declared the use of single blind method. There were no descriptions about concealment of allocation, withdrawals or dropouts.
Figure 2.
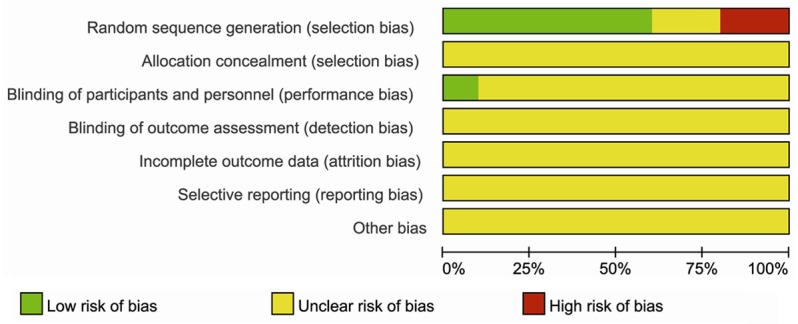
Risk of bias summary: review authors’ judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study.
28-day mortality
Eight studies [9-12,14-16,18] reported the 28-day mortality, data were extracted for meta-analysis. In the eight studies, containing 589 participants, 307 were assigned to the experimental group (TCM plus RT), whereas 281 participants were assigned to the control group (RT). There was no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.99, I2 = 0%), thus the fixed-effect model method was used. The result showed that TCM reduced the 28-day mortality compared to RT (RR = 0.67; 95% CI, 0.51~0.87; P = 0.002) (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
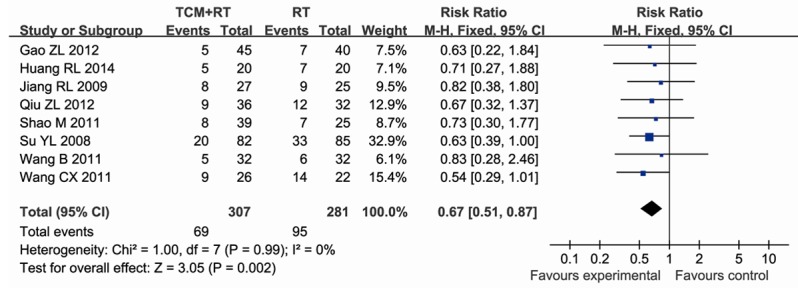
Forest plot showing RR (with 95% CI) for 28-day mortality of eligible studies comparing TCM plus RT with RT alone in a fixed effect model.
Length of ICU stay
Three studies [10-12] reported the length of ICU stay, data were extracted for meta-analysis. In the three studies, containing 295 participants, 153 were assigned to the experimental group (TCM+RT), whereas 142 participants were assigned to the control group (RT). There was no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.41, I2 = 0%), thus the fixed-effect model method was used. The result showed that TCM reduced the length of ICU stay compared to RT (MD = -1.82; 95% CI, -2.60~-1.04; P<0.00001) (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
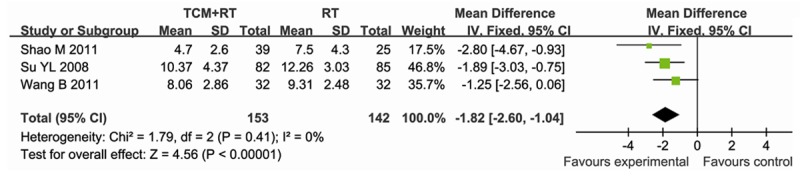
Forest plot showing MD (with 95% CI) for ICU stay of eligible studies comparing TCM plus RT with RT alone in a fixed effect model.
APACHE II score after treatment
Six studies [10-13,16,18] reported the APACHEII score after treatment, data were extracted for meta-analysis. In the six studies, containing 493 participants, 256 were assigned to the experimental group (TCM+RT), whereas 237 participants were assigned to the control group (RT). There was no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.30, I2 = 18%), thus the fixed-effect model method was used. The result showed that TCM reduced the APACHE II score after treatment compared to RT (MD = -2.95; 95% CI, -3.99~-1.91; P<0.00001) (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
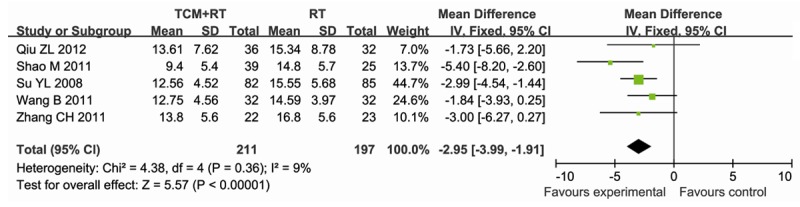
Forest plot showing MD (with 95% CI) for APACHE II score after treatment for overall duration of eligible studies comparing TCM plus RT with RT alone in a fixed effect model.
Serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment
Six studies [11-13,16-18] reported the serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment, data were extracted for meta-analysis. One study [18] was excluded for the heterogeneity it may bring. In the five studies left, containing 529 participants, 262 were assigned to the experimental group (TCM+RT), whereas 267 participants were assigned to the control group (RT). There was no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.5, I2 = 0%), thus the fixed-effect model method was used. The result showed that TCM reduced the serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment compared to RT (SMD = -0.50; 95% CI, -0.68~-0.33; P<0.00001) (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
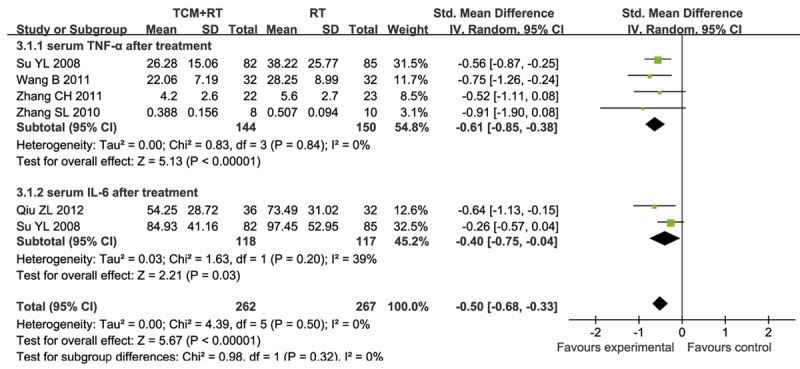
Forest plot showing SMD (with 95% CI) for Serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment of eligible studies comparing TCM plus RT with RT alone in a random effect model.
Of these five studies [11-13,16,17], four studies [11-13,17] reported the serum TNF-α concentration after treatment. 144 of 294 participants assigned to the experimental group (CM) compared with 150 of 294 participants assigned to the control group (WM) (SMD = -0.61; 95%CI, -0.85~-0.38; P<0.00001), with no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.84, I2 = 0%) (Figure 6).
Of these five studies [11-13,16,17], three studies [11,13,16] reported the serum IL-6 concentration after treatment. Data in one study [11] were not used because it used medians as assessment value, while means and SD values were used in others. 118 of 235 participants assigned to the experimental group (TCM+RT) compared with 117 of 235 participants assigned to the control group (RT) (SMD = -0.37; 95% CI, -0.63~-0.11; P = 0.005), with no significant heterogeneity between studies (P = 0.20, I2 = 39%) (Figure 6).
Publication bias
All trials claimed to have randomly assigned participants into different groups, but the details of randomization and concealment methods were rare. The TCM approaches were somewhat heterogeneous because different Chinese medicines were used in different researches. Hence, most of the trails included in this review had a risk of bias. While, there was no evidence of funnel plot asymmetry according to Begg’s test (P = 0.266).
Sensitivity analysis
Pre-specified sensitivity analyses were conducted for the comparison of 28-day mortality (Table 3). The RR of respond was relatively stable when different effect model were used, and bias of trails were moderate. While different routes of administration led to different results (Vianasogastric tube or oral or rectal, RR = 0.64; 95% CI, 0.46~0.89; P = 0.008; Intravenous drip, RR = 0.71; 95% CI, 0.47~1.09; P = 0.11).
Table 3.
Sensitivity analyses of efficacy of TCM on 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis
| Number of studies | Number of subjects | RR | 95% CI | I2 value | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect model | ||||||
| Fixed effect model | 8 | 588 | 0.67 | 0.51 to 0.87 | 0% | 0.002 |
| Random effect model | 8 | 588 | 0.66 | 0.51 to 0.86 | 0% | 0.002 |
| Risk of bias of trails | ||||||
| Moderate | 5 | 391 | 0.69 | 0.50 to 0.94 | 0% | 0.02 |
| High | 3 | 197 | 0.62 | 0.39 to 0.98 | 0% | 0.04 |
| Route of administration | ||||||
| Vianasogastric tube/oral/rectal | 4 | 319 | 0.64 | 0.46 to 0.89 | 0% | 0.008 |
| Intravenous drip | 4 | 269 | 0.71 | 0.47 to 1.09 | 0% | 0.11 |
Discussion
This meta-analysis has demonstrated that TCM plus routine therapy were more effective than routine therapy alone for the treatment of sepsis. Reduction in 28-day mortality, length of ICU stay and APACHE II score after treatment were all of statistics significance. Serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment including TNF-α and IL-6 were assessed and significant decrease was found. In the sensitivity analyses for 28-day mortality, the RR of respond was relatively stable, and TCM administration via vianasogastric tube or oral or rectal (P = 0.008) seems to be more effective compared with intravenous drip (P = 0.11). The different results were probably associated with the gut, an important immunologically active organ which plays an important role in the development of sepsis. The route of administration via oral or rectal was likely to have a directly effect on intestinal and resulted in better intestinal protection.
Sepsis is a life threatening illness which refers to the systemic inflammatory response following micro-bial infection [20]. The early phase of sepsis is generally believed to result from the uncontrolled production of proinflammatory mediators, the so-called “cytokine storm” [21]. Inflammatory cytokines play a very important role in sepsis including TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-10. In our review, serum inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-6) concentration after treatment was decreased and so was the 28-day mortality. TNF was found to be a potent stimulator of the activation of macrophages/monocytes and NK cells, it also induces the production of selectins, platelet activating factor, and intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAM), which mediate neutrophil migration into tissues [22]. Some researches [23,24] also found that high serum TNF-α levels associated positively with the severity of disease and fatal outcome. As for IL-6, a research found that the elevated serum IL-6 levels are associated with increased mortality in participants with intraabdominal sepsis [25]. While, contrary to our study, Florence Riche with coauthors found that high serum TNF levels were correlated with increased survival in abdominal septic shock [26]. Most researchers believe that the intensity of immunoinflammatory response influences the outcome of sepsis and if this reaction is uncontrolled, it can lead to the MODS [27]. Maybe we can not deem that the reason for our delighted outcomes was reducing the inflammatory cytokine, but regulating it to a more appropriate level. Although the long-term effects were unknown, we can expect a better outcome as for the current data.
The possible mechanism of Chinese medicine in treating sepsis are as follows: (1) anti-inflammation and immunoregulation [28]; (2) toxic free radicals clearing [8,29]; (3) circulation improvement; (4) intestinal protection. Some kinds of traditional Chinese medicine have been deeply researched, for example, the rhubarb has been reported to have an antiplatelet aggregation activity, antioxidant activity, and vasorelaxant effects [30], and the detailed mechanisms were reported in several researches [31-33]. Besides, some other effects have been found, for example, preventing TNF-α oversecretion [34,35], promoting gastrointestinal electric activity and intestinal peristalsis, promoting the endotoxin eduction and decreasing the bacteria translocation, improving microcirculation [36,37]. Another commonly used Chinese medicine, Salvia miltiorrhiza, was discussed and reported that different compounds extracted from the medicine have specific activity against leukocyte adhesion, platelet aggregation, the release of oxygen radicals and endothelial cell injury, among other effects associated with the pathogenesis of septic shock, and the possible mechanisms were also disclosed [30]. Salvia miltiorrhiza, another well-researched Chinese medicine, was thought to play key roles in the pathogenesis of septic shock in reducing neutrophil degranulation, oversecretion of prostaglandins (PGs), and the induction of nitric oxide synthase [30]. Meanwhile, two proteins with antifungal activities were isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza recently [38].
This analysis provides a current assessment of the effect of TCM for participants with sepsis. In our analysis, usage of TCM was preferable as a treatment for sepsis in 28-day mortality, length of ICU-stay and APACHE II score after treatment. What’s more, no apparent adverse effects were found in all the studies included. We analyzed the change of serum inflammatory factors concentration after treatment which may be a potential mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for sepsis. We also conducted sensitivity analyses according to effect models, risk of bias of included trials, route of administration to assess whether any of these differences affected overall efficacy, and the probability of different routes of administration leading to different results was found and discussed. Other strengths of our review include a precise clinical question restricted to participants with sepsis rather than all critically ill participants, and each study we included mentioned its diagnosis explicitly. Moreover, all these studies within groups were in the absence of heterogeneous which increased the accuracy of outcomes.
While the limitations of this review, the same with any other meta-analysis, derive from the quality and reporting of the studies included. All the studies were conducted in mainland China, and the source of experimental data is quite narrow. The protocols of the included studies were not available, we don’t know the potential selective report bias. And there were no details about concealment of allocation, blind method, withdrawals or dropouts in these RCTs, which means potential risk of bias. The small number of studies included decreased the reliability and lack of long-term follow-up prevented us from analysing the long term effects.
In conclusion, this meta-analysis suggests that addition of TCM may be a better solution for sepsis compared with using routine therapy alone, especially in a developing country like China, because most TCM are cheap and accessible, which may largely reduce the expenditure for the participants with sepsis. Despite of the gratified results, more high-quality and large-scale trials are expected to confirm these findings and intensive studies are still needed.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the funds of Shanghai Chen-Guang program (10CG40), Shanghai Health Bureau (XYQ2011022), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30772092), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (14ZR1413700) and Science and technology program (social development) of Zhenjiang (SH2014087) and (SH2015039).
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34:17–60. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0934-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb S, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including The Pediatric Subgroup. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:165–228. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vincent JL, Sakr Y, Sprung CL, Ranieri VM, Reinhart K, Gerlach H, Moreno R, Carlet J, Le Gall JR, Payen D Sepsis Occurrence in Acutely Ill Patients Investigators. Sepsis in European intensive care units: results of the SOAP study. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:344–353. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000194725.48928.3a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Opal SM, Laterre PF, Francois B, LaRosa SP, Angus DC, Mira JP, Wittebole X, Dugernier T, Perrotin D, Tidswell M, Jauregui L, Krell K, Pachl J, Takahashi T, Peckelsen C, Cordasco E, Chang CS, Oeyen S, Aikawa N, Maruyama T, Schein R, Kalil AC, Van Nuffelen M, Lynn M, Rossignol DP, Gogate J, Roberts MB, Wheeler JL, Vincent JL ACCESS Study Group. Effect of eritoran, an antagonist of MD2-TLR4, on mortality in patients with severe sepsis: the ACCESS randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;309:1154–1162. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.2194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blackwell TS, Christman JW. Sepsis and cytokines: current status. Br J Anaesth. 1996;77:110–117. doi: 10.1093/bja/77.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang S, Su Q, Wang C. Study on predictors of mortality and risk factors in patients with septic shock. Journal of Traumatic Surgery. 2007;9:8. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:840–851. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1208623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang H, Xu T, Lew in MR. Future possibilities for the treatment of septic shock with herbal components. Am J Emerg Med. 2009;27:107–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang R, Zhang Z, Xu M, Chang X, Qiao Q, Wang L, Meng X. [Effect of Sini decoction on function of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in patients with sepsis] . Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014;26:184–187. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shao M, Liu B, Wang JQ, Tao XG, Zhou SS, Jin K, Zhang CP. Effect of Xuebijing injection on T helper 17 and CD+ CD+ regulatory T cells in patients with sepsis. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011;23:430–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Su YL, Wang H, Zhang SW. Effect of Qishen Huoxue Granule in treating severe sepsis. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2008;28:209–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang B, Wang YQ, Cao SH, Liang Y. Platelet parameters and platelet Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in patients with sepsis and the effect of a joint treatment-plan integrating traditional Chinese and western medicine: a clinical study. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011;23:616–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang CH, Zhou G, Gong X, Zhang R, Qu XG, Zeng C, Liu JL. Effect of Henyan medicinal recipe on the regulation of immunity in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective clinical trial. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011;23:77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang CX, Gao PY, Xie Q. Effect of modified Qianyang Pellet on extravascular lung water and its corrected factors at the early fluid resuscitation stage of septic shock. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2011;31:200–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jiang RL, Lei S, Wang LC, Wu JN, Zhi YH, Wu YC, Zhu MF, Huang LQ, Ye XH. Effect of Shenfu injection on tissue oxygen metabolism in patients with severe sepsis. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. 2009;24:965–967. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Qiu ZL, Ye YP, Zhang N. [Clinical efficacy of Shenfu injection in treating severe sepsis and its effects on serum levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10] . Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012;32:348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang SL, Chen HL, Yin S. Peripheral blood monocyte activation in acute abdominal diseases with sepsis and its treatment with Fufang Qingxia decoction. Journal of Dalian Medical University. 2010;32:294–298. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gao ZL, Yu XQ, Yang M. Clinical trial of treating stress-induced hyperglycemia patients with sepsis by supplementing Qi, Nourishing Yin and promoting blood flow. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012;32:1336–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Higgins JPT, Green S Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester, England; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 20.American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992;20:864–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Ward PA. Harmful molecular mechanisms in sepsis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:776–787. doi: 10.1038/nri2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Surbatovic M, Veljovic M, Jevdjic J, Popovic N, Djordjevic D, Radakovic S. Immunoinflammatory response in critically ill patients: severe sepsis and/or trauma. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:362793. doi: 10.1155/2013/362793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Terregino CA, Lopez BL, Karras DJ, Killian AJ, Arnold GK. Endogenous mediators in emergency department patients with presumed sepsis: are levels associated with progression to severe sepsis and death? Ann Emerg Med. 2000;35:26–34. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(00)70101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shen Y, Cui N, Miao B, Zhao E. Immune dysregulation in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation. 2011;34:36–42. doi: 10.1007/s10753-010-9205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Latifi SQ, Riordan MA, Levine AD, Stallion A. Persistent elevation of serum interleukin-6 in intraabdominal sepsis identifies those with prolonged length of stay. J Pediatr Surg. 2004;39:1548–1552. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2004.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Riché F, Panis Y, Laisné MJ, Briard C, Cholley B, Bernard-Poenaru O, Graulet AM, Guéris J, Valleur P. High tumor necrosis factor serum level is associated with increased survival in patients with abdominal septic shock: a prospective study in 59 patients. Surgery. 1996;120:801–807. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(96)80087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Surbatović M, Radaković S, Jovanović K, Romić P. New strategies in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome therapy for sepsis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2005;133:379–383. doi: 10.2298/sarh0508379s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tan BK, Vanitha J. Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects of some traditional Chinese medicinal herbs: a review. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:1423–1430. doi: 10.2174/0929867043365161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Varon J. Herbal medicine in acute care medicine: past, present, and future. Am J Emerg Med. 2009;27:113–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang H, Xu T, Lewin MR. Future possibilities for the treatment of septic shock with herbal components. Am J Emerg Med. 2009;27:107–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peng SM, Wang SZ, Zhao JP. Effect of rhubarb on inflammatory cytokines and complements in patients with systemic inflammation reaction syndrome and its significance. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2002;22:264–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ko SK, Lee SM, Whang WK. Anti-platelet aggregation activity of stilbene derivatives from Rheum undulatum. Arch Pharm Res. 1999;22:401–403. doi: 10.1007/BF02979065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Toguchida I, Park JY, Harima S, Yoshikawa M. Antioxidant constituents from rhubarb: structural requirements of stilbenes for the activity and structures of two new anthraquinone glucosides. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001;9:41–50. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(00)00215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Du DJ. Chinese herbal medicine and tumor necrosis factor. Sichuan Journal of Physiological Sciences. 1992;2:92–94. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wu CD, Li MZ, Zhang YP. Effects of Reduqing Injection on Plasma TNF-α and IL-6 Levels in Rabbits with Endotoxin-induced DIC. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1995;15:356–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chen DC, Yang JD, Jing BW, Yang XY, Chen XY, Li HH. The impact of rhubarb on gastrointestinal dynamics: basic and clinical research. Chin Criti Care Med. 1997;9:411–413. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen DC, Jing BW, Yang XY, Song ZF, Yan M, Zhao L, Wei HW, Yv KL, Zhang XY, Ma J. The protective effect of rhubarb on gut in critical illness. Chin Criti Care Med. 2000;12:87–90. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lam SK, Ng TB. Isolation of a novel thermolabile heterodimeric ribonuclease with antifungal and antiproliferative activities from roots of the sanchi ginseng Panax notoginseng. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285:419–423. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


