Figure 1.
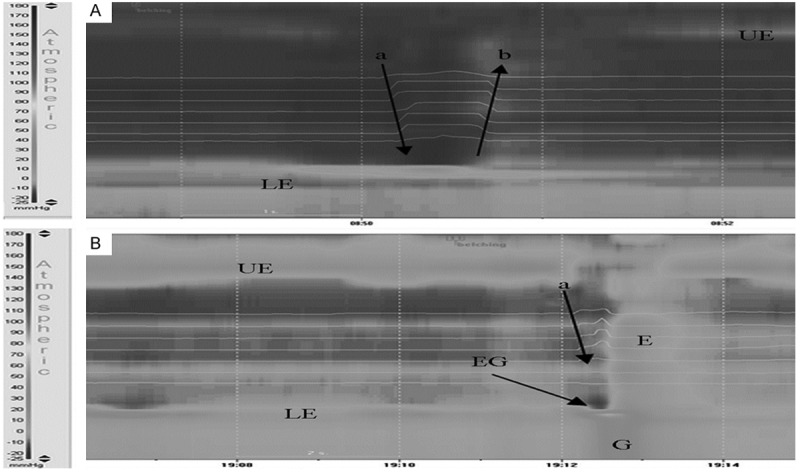
Supragastric belching of non-specific belch patients exhibited in the combined HRM-IMP. A: Air moved rapidly into the esophagus (arrow a) and expelled from oral direction (arrow b) less than 1 second later, without primary or secondary esophageal peristalsis, while associated with the contraction of abdominal muscles and diaphragm; B: Air moved rapidly into the esophagus (arrow a). The abdominal contraction led to the esophageal and gastric internal pressure increased. The diaphragmatic contraction made the EGJ move distally, which decreased the pressure within the esophagus. Notes: UES, upper esophageal sphincter; LES, lower esophageal sphincter; EGJ, gastroesophageal junction; E, esophagus; G, stomach; Arrows indicated the directions of gas movement.
