Fig. 3.
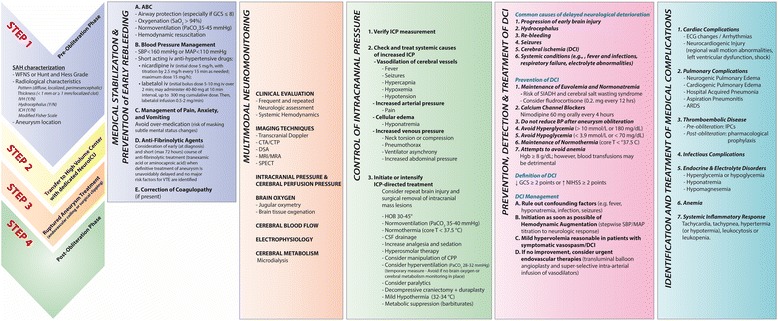
Summary of a possible approach for the management of subarachnoid haemorrhage patients in poor neurological condition. ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, BP blood pressure, CPP cerebral perfusion pressure, CSF cerebrospinal fluid, CTA/CTP computed tomography angiography/computed tomography perfusion, DCI delayed cerebral ischaemia, DSA doxyl stearic acid, ECG electrocardiogram, GCS Glasgow Coma Scale, Hgb haemoglobin, HOB head of bed, ICH intracerebral haemorrhage, ICP intracranial pressure, IPC intermittent pneumatic compression, iv intravenously, IVH intraventricular haemorrhage, MAP mean arterial pressure, MRI/MRA magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography, NeuroICU neurointensive care unit, NIHSS National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score, PaCO 2 arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide, SaO 2 arterial oxygen saturation, SBP systolic blood pressure, SIADH syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone, SPECT single-photon emission computed tomography, T temperature, VTE venous thromboembolism, WFNS World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies
