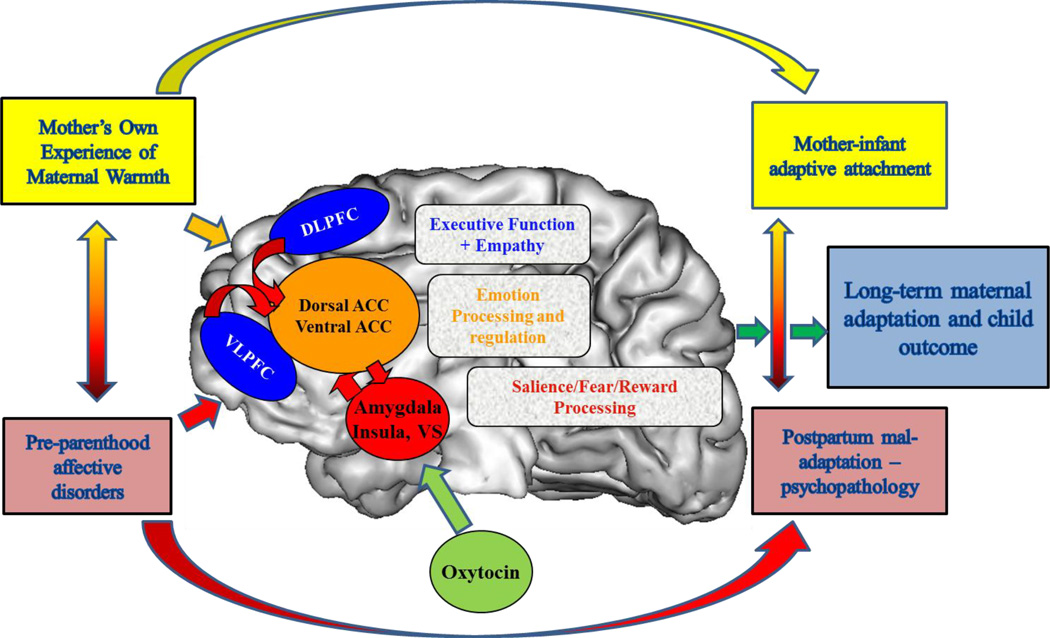
Figure 1.
Plasticity in the maternal brain - Early life factors, such as experience of parental warmth and previous mental health affect plastic brain circuits that ultimately regulate maternal affective regulation capacity and caregiving outcomes. Plastic or adaptable circuits, some of which are overlappping, include those for Emotion Response and Processing [Amygdala, Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC), Ventral ACC] and Salience/Fear/Motivation Processing [Amygdala, Insula, Ventral Striatum (VS)] working with cortical executive function [Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex (VLPFC), Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC)] and empathy [Medial Prefrontal Cortex (MPFC), Precuneus, Superior Temporal Sulcus) circuits (adapted from Moses-Kolko et al., 2014).