Figure 1. Identification of Tuba1aND/ND mouse model.
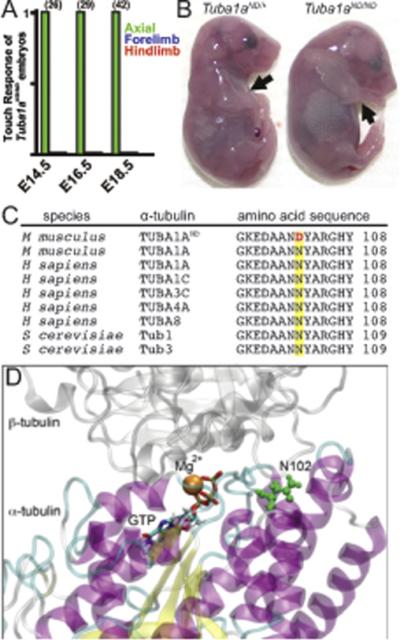
(A) Touch assay to examine movement at embryonic days E14.5 (n=26 embryos), E16.5 (n=29), and E18.5 (n=42) of mouse development shows loss of locomotor movement in Tuba1aND/ND mutants. (B) Morphology of E18.5 littermates. Tuba1aND/ND mice have extended hindlimbs and forelimbs (black arrows) and a hunched back. (C) Asparagine residue 102 in a conserved region of α-tubulin is mutated to an aspartic acid (red letter) in Tuba1aND/ND mice. (D) Location of N102 (green residue) in the tubulin intradimer interface. N102 resides near the GTP N-site and Mg2+ binding site of α-tubulin.
