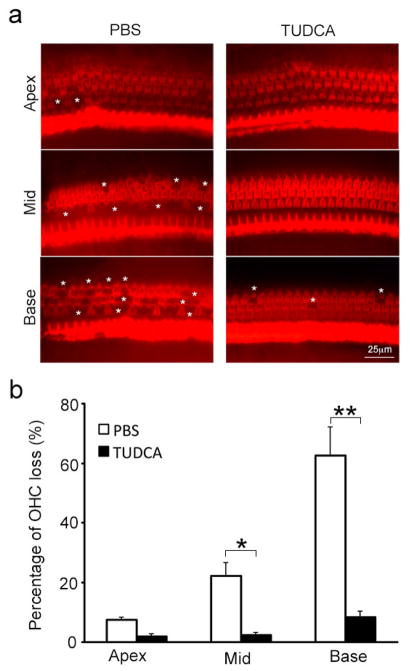
Fig. 3.
TUDCA prevents OHC loss in erl mice at 10 weeks of age. (a) The whole-mount preparations from the apex, middle, and basal turns of the cochleae were stained for F-actin. Obvious OHC loss was observed in the basal and middle turns, and a small amount of OHC loss was found in the apical turn in the PBS-treated mouse. Very minimal OHC loss was found in the TUDCA-treated mouse. White stars indicate areas of OHC loss. (b) The mean percentages of OHC loss are shown for each turn of the cochleae in the PBS and TUDCA groups at 10 weeks of age. Compared to the TUDCA group, the PBS group exhibited a higher percentage of OHC loss in the middle and basal turns. Data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m (n = 3 mice per group). **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, student t-test.