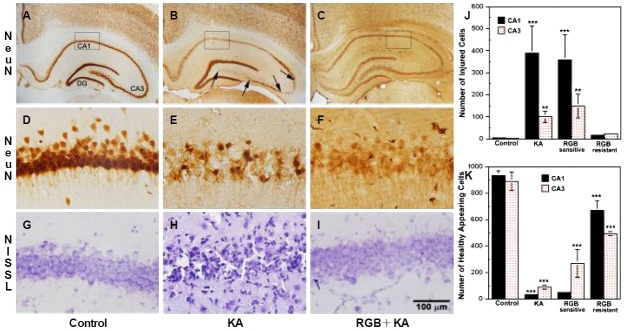
Figure 3.
Histological examination 28 days after KA ± RGB treatment at the level of the hippocampus. (A, D), Control NeuN labeling was intense and uniform throughout the hippocampal subfields; high magnification of CA1 labeled neurons showed they were round and healthy (400×). (B, E), After KA (15 mg/kg, i.p.), extensive cell loss was observed throughout the CA1, CA3, and hilar subfields (between arrows); the DG and CA2 were relatively resistant. High magnification revealed fewer, shrunken CA1 neurons throughout the layer; CA3 and hilar neurons were shrunken or absent. (C, F), Partial injury to CA1 and CA3 neurons was revealed after 2× RGB (5 mg/kg, i.p.) followed by KA; high magnification presented many healthy neurons. (G), Nissl staining of control animal labeled healthy, round CA1 neurons. (H), Nissl staining of KA animal revealed marked injury to CA1 neurons. (I), RGB+KA animals that were resistant to seizures displayed little or no injury, resembling the controls. (J, K), Graphic analyses of the number of injured vs. healthy appearing pyramidal cells at 3 and 28 days following systemic injections of both groups of animals that were either sensitive or resistant to seizures. Bars represent the mean averages ± SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01. One Way ANOVA. Scale=100 μm. KA, kainic acid; RGB, retigabine; DG, dentate gyrus; NeuN, neuronal nuclear antigen.