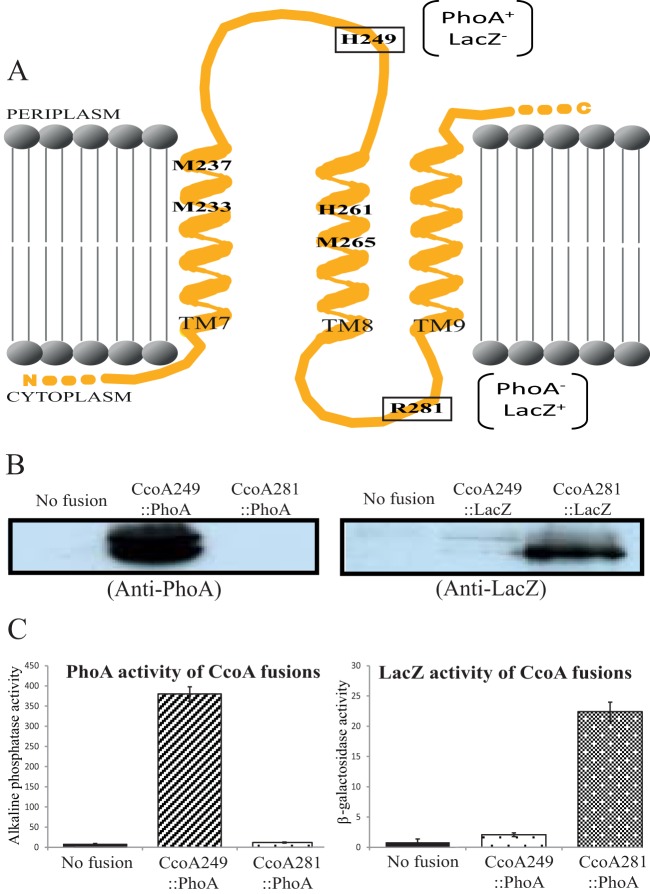
FIG 2 .
Membrane topology of the TM7, -8, and -9 of R. capsulatus CcoA. (A) The TMRPres2D program predicted topology of the TM7, TM8, and TM9 of CcoA was used to fuse LacZ and PhoA to His249, located between TM7 and TM8, and to Arg281, located between TM8 and TM9. The conserved residues Met233, Met237, His261, and Met265, located in TM7 and TM8, and the PhoA and LacZ phenotypes of the fusions are indicated. (B) Immunoblot analysis of CcoA-PhoA and CcoA-LacZ fusions. Chromatophore membranes from cells carrying no fusion (ΔccoA) or the CcoA-LacZ (CcoA249::LacZ and CcoA281::LacZ) and CcoA-Pho (CcoA249::PhoA and CcoA281::PhoA) protein fusions were probed with polyclonal antibodies against E. coli alkaline phosphatase (anti-PhoA) or β-galactosidase (anti-LacZ), as indicated. The double band seen with the CcoA249::PhoA fusion protein was attributed to proteolytic degradation (38). (C) β-Galactosidase (for the CcoA-LacZ fusions) and alkaline phosphatase (for the CcoA-PhoA fusions) activities of chromatophore membranes of R. capsulatus cells harboring the appropriate fusions.