Table 4.
TRUNK POSITION
| NEUROMUSCULAR | ||||
| DEFICIT: Excessive trunk flexion and/ or rounding (kyphosis) of the lumbar spine during squat. | ||||
| TARGETED CORRECTION: Improve awareness for and proprioception of appropriate trunk angle parallel to tibias and neutral, slight lordosis lumbar spine position. | ||||
| Exercise | Description | Purpose | Cue | Example |
| 1. Cat/Cow | Assume quadruped position on knees and hands. Practice alternating from rounded back posture to arched back posture. | Identify difference between lordotic and kyphotic positions. | "Dip spine down and round spine up" |  |
| 2. Ball Wall Squat | Pin a ball (similar to small Swiss ball) between the lower back and wall. Squat down while keeping ball pinned against the wall. The ball will roll up to the shoulder blades. Ascend and repeat. | Exercise facilitates a more vertical trunk position because horizontal force from wall serves as assistance. Ball rolling encourages the correct spinal curve. | "Slide down the ball" |  |
| 3. Pole Squat and Fix | Perform squat near a sturdy pole or column. At apex of squat, use column as assistance to pull torso into correct position and hold. Heels must remain on the ground. | Assistance to help athlete self-generate and learn correct deep hold position. | "Hold pole and fix" |  |
| STRENGTH/ STABILITY | ||||
| DEFICIT: Inadequate core strength to maintain torso parallel to tibias and lack of lower back tightness to generate stability. May be due to trunk extensor weakness and hip extensor weakness. | ||||
| TARGETED CORRECTION: Improve trunk stability, trunk extensor strength and hip extensor strength to maintain slightly extended lordotic position and trunk parallel to the tibias throughout the squat. | ||||
| Exercise | Description | Purpose | Cue | Example |
| 1. Plank | Hold plank position with emphasis on maintaining lordosis throughout exercise. | Improve isometric strength of the back musculature and promote correct lumbar spine position. | "Straight as an arrow" |  |
| 2. Superman | Lay flat on stomach with your arms straight out in front and legs straight out behind. Keep arms and legs shoulder-width apart for the duration of the exercise. Lift your legs and arms simultaneously at least 6 inches off the ground. Keep each movement slow and controlled to prevent pulling muscles. | Strengthen the lower back musculature. | "Raise chest and arms together" | 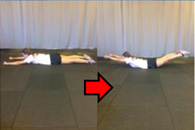 |
| 3. Overhead Squat | Perform squat with dowel in overhand grip overhead with elbows extended. | Strengthen back musculature and promote erect trunk during squat. | "Keep the dowel behind your eyes" |  |
| MOBILITY | ||||
| DEFICIT: Lack of mobility of the hip flexors (iliopsoas) and trunk flexors (abdominals). | ||||
| TARGETED CORRECTION: Improve spinal extension mobility to assume and maintain slight lordosis posture. Mobility of trunk flexors and hips flexors necessary for appropriate trunk angle. | ||||
| Exercise | Description | Purpose | Cue | Example |
| 1. Standing Back Arch | Stand up straight with hands on hips and thumbs on the lower back. Extend hips forward and push abdomen forward, while maintaining a slight arch in back. Hold for 10 seconds. | Improve hip flexor mobility. | "Push hips forward" | 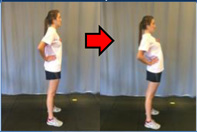 |
| 2. Cobra | Lay on stomach with hands flat just outside of the shoulders. Extend elbows to lift torso off of ground. Place small arch in lower back and pull shoulders slightly backward. Keep hips on the ground for this exercise. Hold for 10 seconds. | Improve trunk flexor mobility. | "Lengthen your abdomen" |  |
| 3. Chaturanga | Begin in downward dog position. Extend hips, bend elbows, and lower torso into push-up position. Push up into cobra position by arching back and raising chest. Keep hips elevated off of the ground for this exercise. Reverse back into push-up position and then back to downward dog. | Improve trunk flexor mobility and core strength. | "Smoothly transition between each position" |  |
