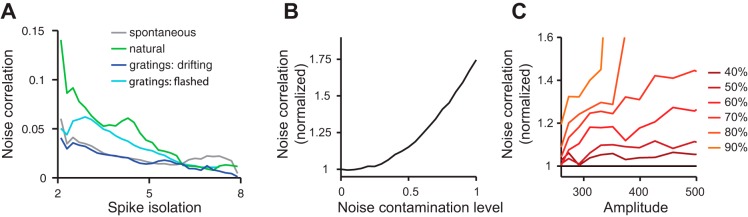
Fig. 6.
Effect of spike isolation on noise correlations. A: dependence of noise correlations on spike isolation. B: modulation of noise correlations by varying the multiunit (“noise”) contamination level of single units. C: modulation of noise correlations as a function of spike amplitude at different contamination levels with multiunit spikes. Note that at high contamination levels (>70%), the full range of amplitudes cannot be sampled due to the small average amplitude of multiunit spikes.