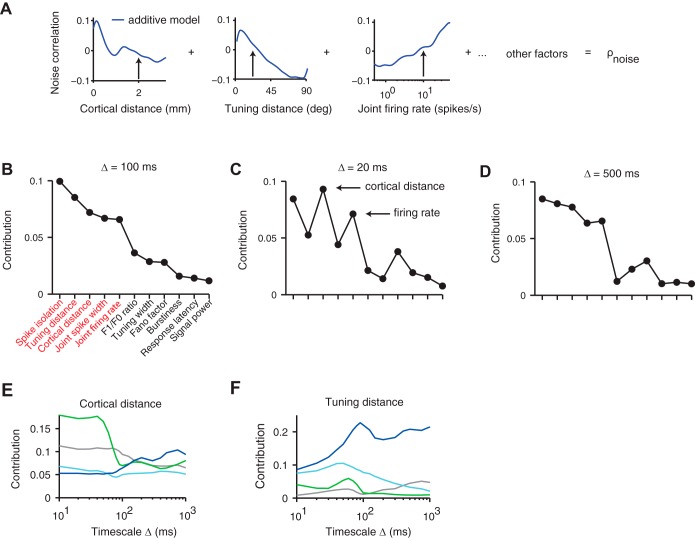
Fig. 7.
Use of a nonlinear additive model to rank the role of multiple factors in noise correlations. A: in the model, each pair of neurons is associated with eleven factor values. The model predicts their noise correlation by summing the function values of 11 one-dimensional functions corresponding to those factors. B: ranking of factors according to their contribution to noise correlations averaged over all 4 stimulus types (Δ = 100 ms). C and D: a largely similar ranking was seen at 2 different timescales (Δ = 20 ms, 500 ms). E: contribution of the cortical distance factor as a function of timescale for each stimulus condition. F: same as E but with tuning distance factor.