Fig. 1.
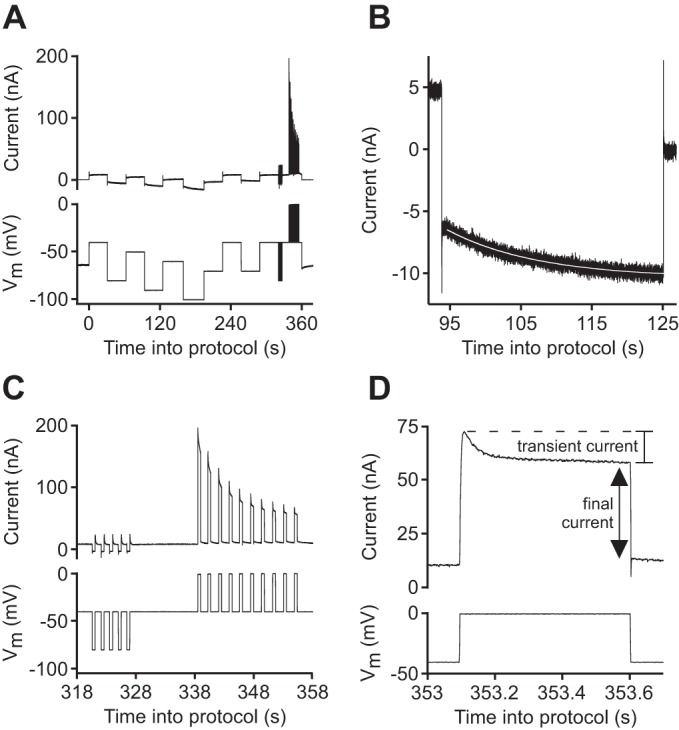
Protocol for measuring membrane potential (Vm), neuron input resistance (RN), hyperpolarization-activated current (Ih) time constant, and transient and sustained (“final”) depolarization-activated currents. A and C: approximately every 10 min, the electrometer was switched into 2-electrode voltage clamp, and (in lobster) a series of 30-s steps was commanded to various voltages, followed by (in lobster and leech) 5, 0.5-s steps from −40 to −80 mV and then 10, 0.5-s steps from −40 to 0 mV. Vm was measured just before the cell was clamped. B: the slow changes in current that occurred during the 30-s steps in lobster were used to calculate Ih time constants. Therefore, we fitted (white line running through data) these changes with a single exponential to measure Ih time constant as a function of Vm. C and D: the 0.5-s hyperpolarizing steps were used to calculate RN and the last 5 of the depolarizing steps to measure the transient and final currents.
