Fig. 6.
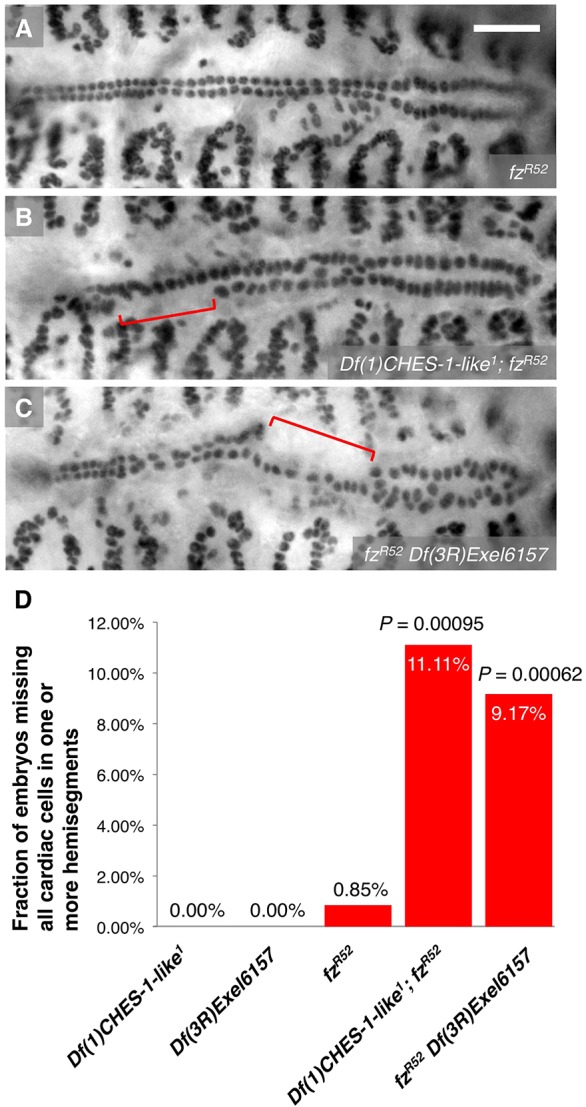
Synergistic genetic interactions between CHES-1-like and fz, and between jumu and fz. (A-C) Mef2 antibody staining of CCs, illustrating the presence or absence of the MCH phenotype (square brackets), in representative Stage 16 embryos that are (A) homozygous for fzR52, a strong hypomorphic mutation of fz, (B) doubly homozygous for both the fz mutation and the CHES-1-like null mutation, and (C) doubly homozygous for both the fz mutation and the jumu null deficiency. Whereas the MCH phenotype is rarely detected in the fzR52 homozygotes, embryos doubly homozygous for the fz mutation and one of the Fkh gene mutations exhibit significant instances of the MCH phenotype. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Quantification and significance of the MCH phenotypes. From left to right, the P-values indicate the difference between the phenotype of embryos doubly homozygous for the fz and CHES-1-like mutations and the additive effects of the phenotypes in fz homozygotes and CHES-1-like homozygotes; and the difference between the phenotype of embryos doubly homozygous for the fz mutation and the jumu null deficiency and the additive effects of the phenotypes in fz homozygotes and jumu homozygotes.
