Fig. 6.
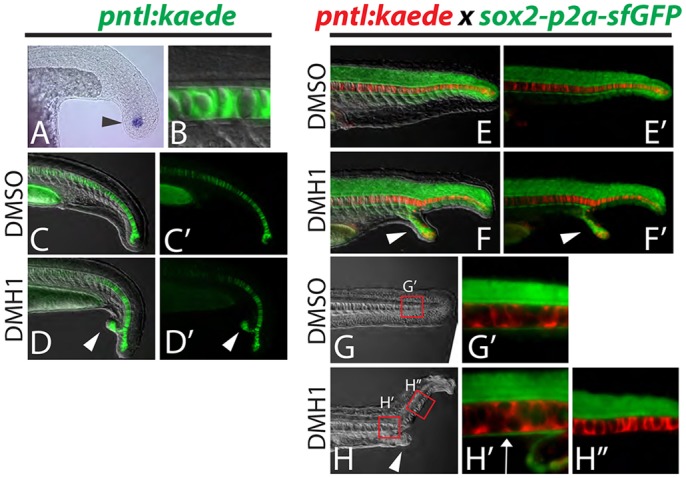
Dorsal and ventral MPCs separate in embryos with ectopic tails. (A-D′) A newly created transgenic reporter line (pntl:kaede) exhibits kaede mRNA expression in notochord progenitor cells (A, arrowhead) and Kaede protein perdures in the notochord only (B). Ectopic tails always contain notochord cells (D,D′, arrowheads). (E-H″) Notochord and hypochord were visualized simultaneously by crossing the pntl:kaede line to the sox2-p2a-sfGFP line and photoconverting the Kaede from green to red. Analysis of ectopic tails at 24 hpf revealed that the hypochord is diverted from the primary midline into the ectopic tail (F,F′, arrowheads). At 36 hpf it is clear that the hypochord is present anterior to the ectopic tail (ectopic tail is pictured in H, arrowhead) as labeled by sfGFP driven by the sox2 locus (H′, arrow), but is absent in the primary midline posterior to the ectopic tail (H″).
