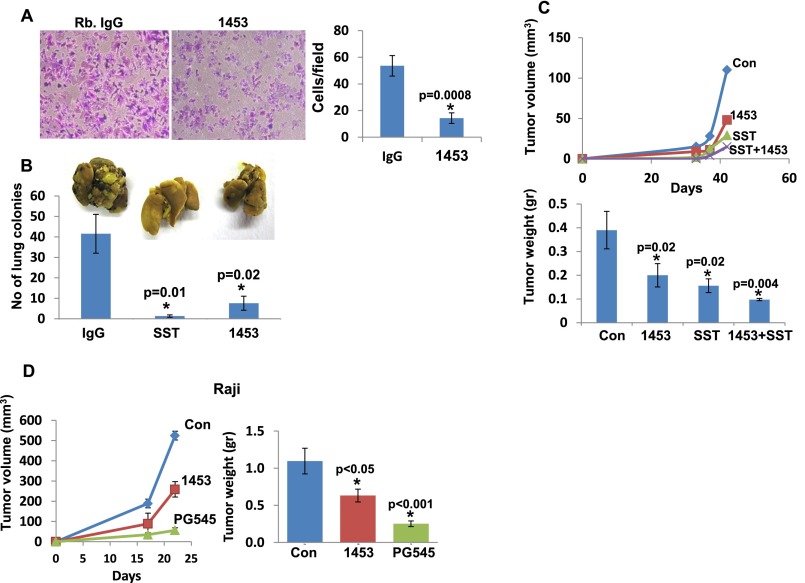
Fig. S2.
Anti-heparanase neutralizing polyclonal Ab 1453 attenuates cell invasion, metastasis, and tumor growth. (A) Cell invasion. U87 glioma cells (2 × 105) were plated onto Matrigel-coated 8-μm Transwell filters in the presence of rabbit IgG or Ab 1453 (2 μg). Invading cells adhering to the lower side of the membrane were visualized after 6 h (*P = 0.0008). (B) Tumor metastasis. Mouse B16 melanoma cells (1.5 × 105) were inoculated into the tail vein of C57BL/6 mice (n = 7), together with rabbit IgG (300 µg), Ab 1453 (300 µg), or SST0001 (400 µg). Lungs were harvested after 18 d, fixed in Bouin's solution, and photographed (Inset), and the number of metastatic lesions was counted (P = 0.01 and 0.02 for Con vs. SST0001 and Con vs. Ab 1453, respectively). (C) Tumor growth. U87 glioma cells (5 × 106/0.1 mL) were inoculated s.c. at the right flank of 5-wk-old female SCID mice (n = 7). Mice were administrated with Ab 1453 (250 µg/mouse every other day), SST0001 (400 µg/mouse twice daily), or both compounds starting 2 d after cell inoculation. Control mice were administrated with PBS. Xenograft size was determined twice a week by externally measuring tumors in two dimensions, using a caliper, and tumor volume was calculated (Upper). At the end of the experiment, xenografts were removed, weighed (Lower), and fixed in formalin. Note the reduced tumor development after heparanase inhibition (P = 0.02, 0.02, and 0.004 for control vs. 1453, control vs. SST0001, and control vs. 1453+SST0001, respectively). (D) Lymphoma tumor growth. Raji cells (5 × 106) were implanted s.c. in SCID mice (n = 6), and mice were administrated with Ab 1453 (250 µg/mouse; every other day), PG545 (20 mg/kg; once a week), or control vehicle (PBS), and tumor growth was inspected over time (Left). At termination, tumors were harvested, weighed (Right), and fixed in formalin for subsequent histological examination.