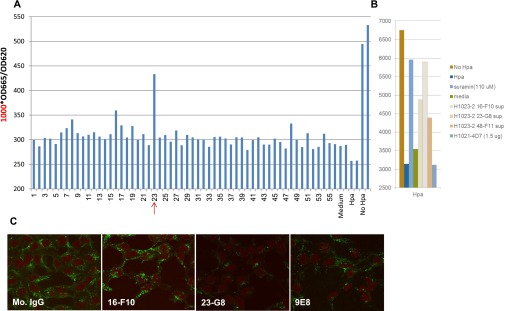
Fig. S4.
Generation of H1023 heparanase-neutralizing mAb. Mice were immunized with human heparanase, and the resulting hybridomas were screened for their ability to bind heparanase by ELISA. Supernatant of the indicated hybridoma was evaluated for heparanase inhibition, using a high-throughput heparanase activity assay (Cisbio Bioassays HTRF). The HTRF heparanase assay is based on HS substrate labeled with both biotin and Eu3+ Cryptate. Active heparanase enzyme cleaves the substrate, causing the loss of energy transfer, and thus a reduction in emissions. High readings therefore represent low heparanase activity. Hybridoma 23 emerged to neutralize heparanase activity (A), and heparanase neutralization was recapitulated by clone H1023 23-G8 (B) used for subsequent experiments. (C) Heparanase-transfected 293 cells were grown with control mouse IgM or the indicated mAb for 2 d. Cells were then fixed with methanol and subjected to immunofluorescent staining applying anti-heparanase Ab.