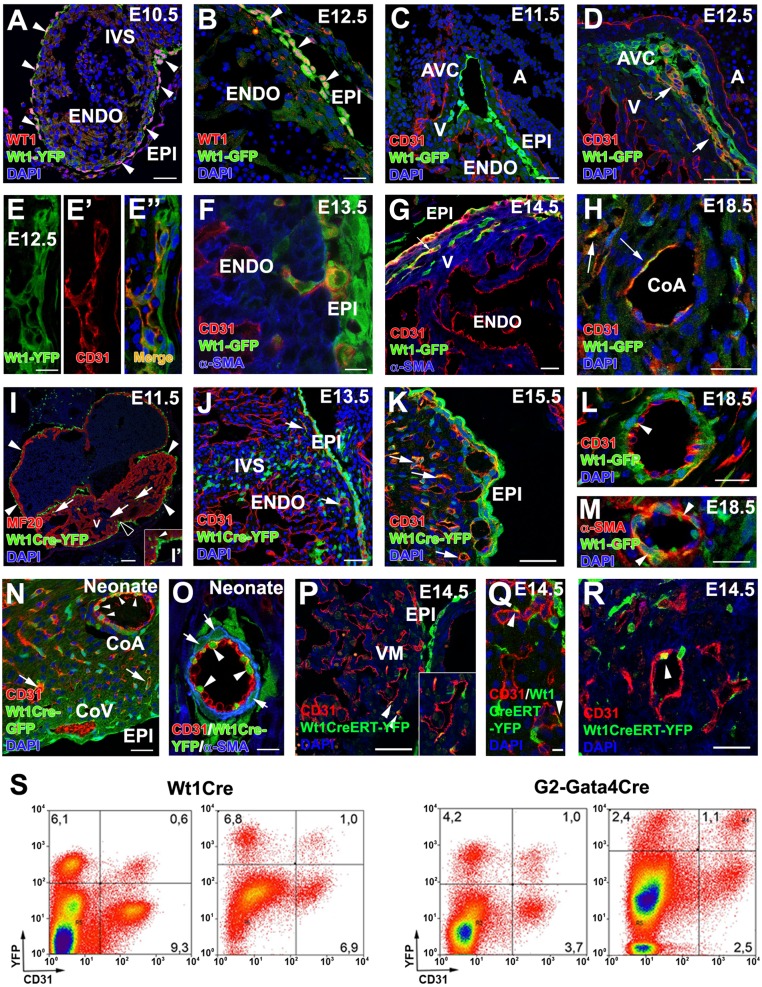
Fig. 2.
Wt1-expressing cells and their progeny contribute to CoE. (A and B) WT1 protein is ubiquitously expressed in epicardial cells and EPDCs at E10.5–E12.5, extensively overlapping with Wt1 promoter-driven GFP expression (arrowheads). (C–G) Reporter expression in Wt1GFP embryos can be observed in the CD31+ subepicardial (E–E”) and intramyocardial (F and G) coronary vasculature at E12.5–E14.5 (arrows in D and G), but not at earlier developmental stages (C). (H) A few Wt1GFP+/CD31+ cells are still found at perinatal stages (arrows). (I, I′, and J) Early Wt1CreYFP+ cells form the epicardium (arrowheads in I; the area marked with a black arrowhead is magnified in I′) and the first EPDCs (arrows in J). At E11.5 many Wt1CreYFP+ epicardial cells show morphological EMT features (arrowhead in I′). (J and K) The lineage reporter colocalizes with the vascular marker CD31 in the subepicardial and intramyocardial coronary plexus between E13.5 (J) and E15.5 (K) (arrows). (L–O) Perinatal (L and M) and neonatal (N and O) hearts show Wt1CreYFP+ cells incorporated in the CoE (arrowheads in L and O) and CoSM layers of large CoA (arrowheads in M and arrows in O) as well as in capillaries (arrow in N). (P–R) Wt1CreERT2;Rosa26-YFP embryos induced with tamoxifen at E9.5 show YFP+ cell incorporation in coronary vessels at E.14.5 (arrowheads). (S) Representative cytograms of dissociated ventricles from midgestation embryos and neonates. Numbers indicate percentages of total events. Both the Wt1CreYFP+ and G2CreYFP+ populations include CD31+ in cells. A, atrium; AVC, atrio–ventricular canal; CoA, coronary artery; CoV, coronary vein; ENDO, endocardium; EPI, epicardium; IVS, interventricular septum; V, ventricle. (Scale bars: 100 µm in I; 50 µm in A, C, D, J, M, N, and P; 25 µm in B, F–H, K, and L; 25 µm in R; 10 µm in E–E′′ and O; 5 µm in Q.)