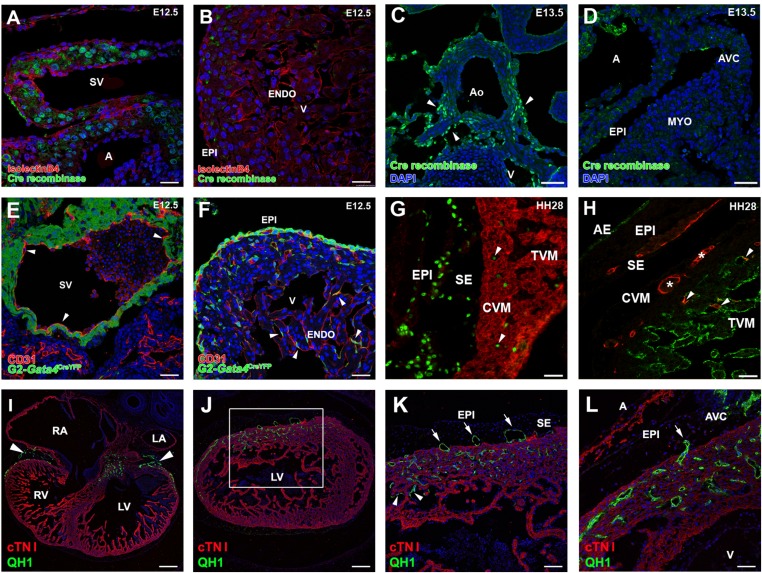
Fig. S1.
Origin and vascularizing properties of ST/PE-derived endothelial cells. (A–D) Cre recombinase expression in G2CreYFP embryos is evident in the inflow myocardium at E12.5 (A) and in the aortic walls at E13.5 (C, arrowheads) but not in the epicardium at E12.5 (B) or epicardium or myocardial layers at E13.5 (D). (E and F) In G2CreYFP embryos, the sinus venosus endocardium is YFP− (arrowheads in E). Some G2-Gata4CreYFP+/CD31+ cells also can be found incorporated in the ventricular endocardium (arrowheads in F). (G) Incorporation of PE-derived endothelial cells in the ventricular endocardium also occurs in quail-to-chick PE chimeric transplantations. PE derivatives, which express the quail pan-nuclear marker QCPN (green), invade the myosin-expressing ventricular walls (MF20+, red); some of these cells are incorporate in the ventricular endocardium (arrowheads). (H) The endothelial nature of these quail PE-derived cells is confirmed further by their expression of the QH1 endothelial marker (red). After FITC-conjugated Lens culinaris agglutinin counterstaining of the endocardium (green), PE-derived CoE cells (asterisks) can be distinguished easily from those that fused with the endocardium (arrowheads). (I–L) Transplantation of posterior pericardiac mesenchyme without PE tissue (homologous to the mammalian ST) extensively vascularizes the embryonic myocardium (green QH1+ cells in I and J; arrowheads in I mark the accumulation of these cells at the atrioventricular canal). The area boxed in J is magnified in K to show endothelial invasion of the myocardial layers (red, cTNI+) from the subepicardial space (arrows). The same phenomenon is also evident at the atrioventricular canal (arrow in L). Some ST-derived endothelial cells also are incorporated in the endocardium (arrowheads in K). A, atrium; AE, atrial endocardium; AVC, atrioventricular canal; CVM, compact ventricular endocardium; ENDO, endocardium; EPI, epicardium; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; SE, subepicardium; SV, sinus venosus; TVM, trabeculated ventricular myocardium; V, ventricle. (Scale bars: 25 µm in A and B; 50 µm in C–H and L; 150 µm in I and J; 75 µm in K.)