Fig. 2.
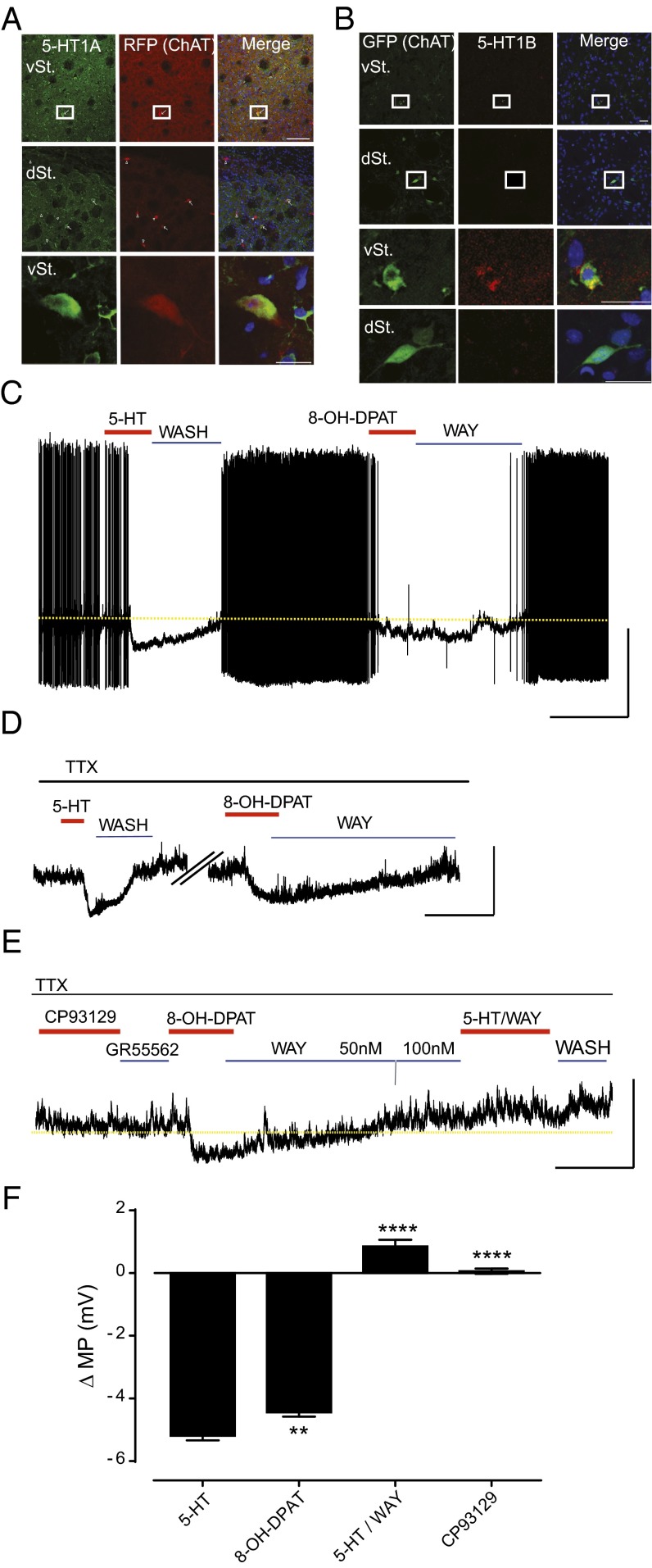
5-HT–induced hyperpolarization of vSt ChIs is mediated by 5-HT1A. (A) Representative immunolabeling images of 5-HT1A in the dSt and vSt of ChATCre; ROSA26Tdtomato mice. [Scale bars, 100 µm (boxes in top rows) and 20 µm (enlarged in bottom rows).] RFP, red fluorescent protein. (B) Representative immunolabeling images of 5-HT1B in the dSt and vSt of ChATEGFP (n = 4 mice). (Scale bars, 20 µm.) (C) Perforated-patch recording in current-clamp configuration from vSt ChIs demonstrating baseline tonic activity, 5-HT bath application (30 μM, 60 s) and washout, and 8-OH-DPAT (selective 5-HT1A agonist) bath application (10 μM, 2 min) followed by reversal with WAY100635 (selective 5-HT1A antagonist, 50–100 nM, 10 min). Note that the dashed line represents the baseline resting membrane potential extrapolated from the control conditions. [Scale bars, 5 min (x axis) and 20 mV (y axis).] (D) Membrane potential (MP) hyperpolarization induced by 5-HT (30 μM) and 8-OH-DPAT (10 μM) in the presence of TTX. [Scale bars, 5 min (x axis) and 10 mV (y axis).] (E) CP93129 (5-HT1B agonist) and GR55562 (5-HT1B antagonist) (both 10 μM/5 min) have no effect on MP, and 5-HT–induced hyperpolarization is completely blocked by pre-exposure to WAY100635. [Scale bars, 5 min (x axis) and 10 mV (y axis).] (F) Summary of ΔMP (mV) for vSt ChIs exposed to 5-HT (n = 23), 8-OH-DPAT (n = 24), and 5-HT following pre-exposure to WAY10635 (n = 6) and CP93129 (n = 6). Bars represent means ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 vs. 5-HT.