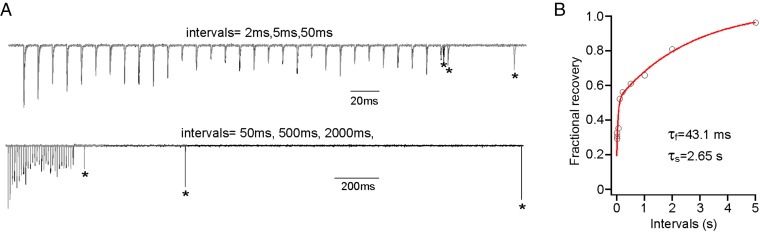
Fig. 8.
Recovery time course from 100 Hz induced steady-state depression. (A) Example traces showing the protocol to measure the recovery time course. Test pulses (indicated by asterisks) were given at different time intervals after 30 stimuli at 100 Hz. Stimulus trains were separated by at least 30-s resting time to allow full recovery between tests. All traces are normalized to the first EPC of each train. Examples for intervals of 2 (black), 5 (dark gray), and 50 ms (light gray) are overlaid and shown in Upper. Examples for intervals of 2 s (black), 500 ms (dark gray), and 50 ms (light gray) are overlaid and shown in Lower. (B) Biexponential fit to the fractional recovery vs. time interval plot. Each data point represents the average from 8 to 20 cells. Error bars are excluded for clarity.