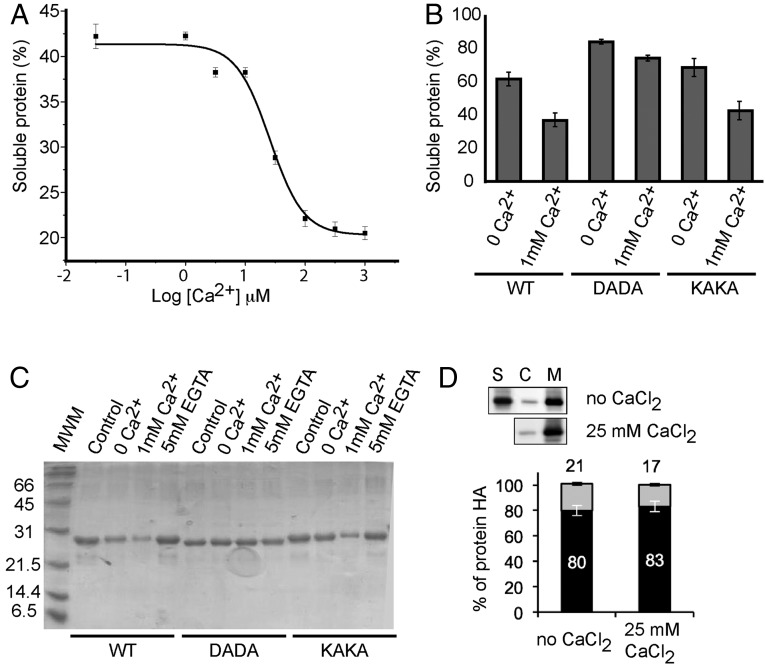
Fig. 4.
In vitro membrane binding and subcellular localization of CAR proteins. (A) Calcium-dependent lipid cosedimentation assays with CAR4. The protein was incubated with liposomes in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ca2+. (B) Comparative analyses of phospholipid binding of wild-type CAR4 and mutants at the Ca2+-dependent lipid binding site CAR4-DADA and the polybasic lipid binding site CAR4-KAKA. Protein quantifications of the soluble fraction after lipid pelleting on A and B were performed by measuring the optical density at 280 nm on a spectrophotometer. Lipid binding activity is expressed as the percentage of the unbound protein to lipids. The differences in the percentage of soluble protein in A and B are explained by the different protein concentration used in the experiments (Materials and Methods). Error bars indicate the SD calculated from three independent measurements. (C) A representative Coomassie blue-stained SDS/PAGE corresponding to the experiments shown in B. (D) Quantification of the subcellular location of CAR4 in the presence or absence of free Ca2+; S, C, and M represent the nonnuclear protein fraction, the cytosolic fraction, and the microsomal fraction, respectively. Immunoblot signals obtained in D were captured using the image analyzer LAS3000, and quantification of the protein signal was done using Image Guache version 4.0 software.