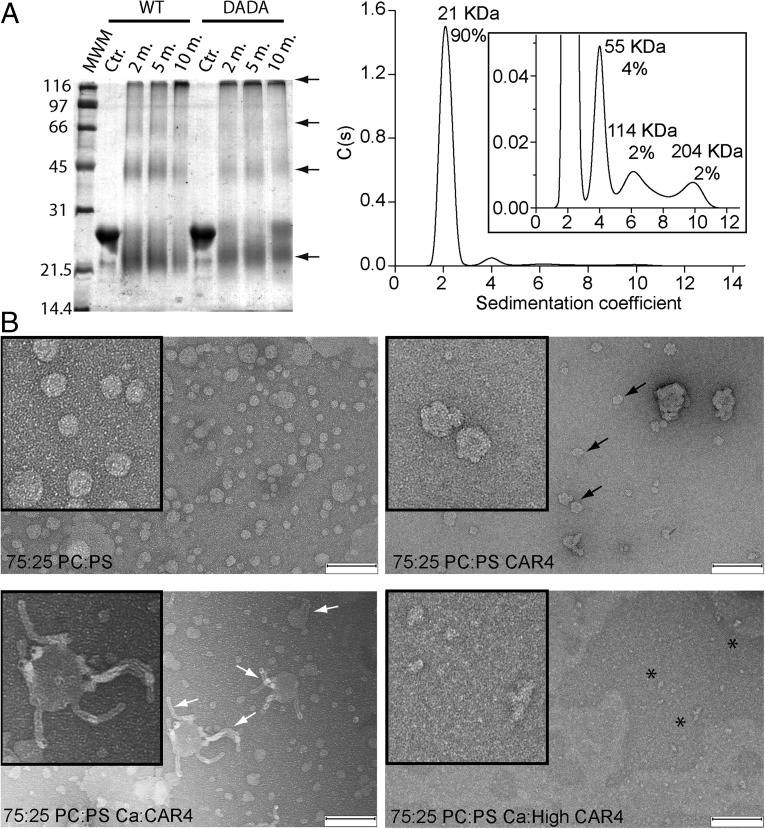
Fig. 6.
(A) CAR4 forms oligomeric structures in solution. (Right) Chemical cross-linking assays for self-association of CAR4 and CAR4-DADA. A Coomassie blue-stained SDS/PAGE showing the cross-linked species by 0.05% glutaraldehyde at different times in minutes. Cross-linked species as well as the monomer migrate aberrantly and are highlighted with arrows. (Left) Analytical ultracentrifugation analysis for CAR4 in native conditions and sedimentation coefficient c(s) distribution. The Inset corresponds to a zoomed area of the distribution. The position and the area under each peak reveal the molecular weight and the relative abundance of the CAR4 oligomers. (B) CAR4 binds to the periphery of liposomes and generates membrane tubules in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Negative-stain transmission electron micrographs of 12.5 μM liposomes (Upper Left) incubated with 8 μM CAR4 (Upper Right), 0.08 μM CAR4 plus 1 mM Ca2+ (Lower Left), and 8 μM CAR4 plus 1 mM Ca2+ (Lower Right). Peripherally membrane-bound CAR4 produces roughness on the surface of the liposomes and is indicated with black arrows, liposome tubules with white arrows, and protein aggregates as black asterisks. (Scale bar, 200 nm.)