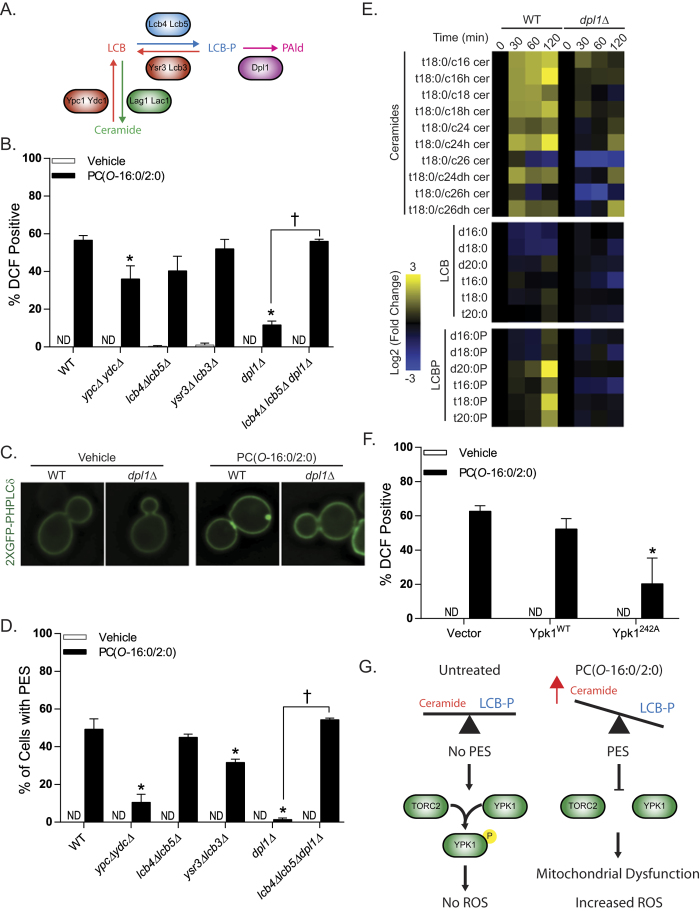
Figure 3. PC(O-16:0/2:0)-dependent inhibition of TORC2-Ypk1 signaling to the mitochondria contributes to ROS production.
(A) Simplified representation of sphingolipid metabolic pathway in yeast. (B) Identification of ceramide metabolism mutants involved in ROS generation. Wild type (WT, BY4741), ypc1Δ ydc1Δ (YKB3271), lcb4Δ lcb5Δ (YKB3273), ysr3Δ lcb3Δ (YKB3305), dpl1Δ (YKB3306) and lcb4Δ lcb5Δ dpl1Δ (YKB3927) strains were grown to mid-log, treated with PC(O-16:0/2:0) (20 μM, 15 min) and labeled with H2-DCFDA (10 μM). (C) and (D) ROS-deficient ceramide mutants do not exhibit PES formation. The subcellular localization of PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools were assessed in the indicated strains expressing a GFP-tagged PtdIns(4,5)P2 probe as previously done (pRS416-GFP2xPHPLCδ)16. Redistribution of the probe was not detected (ND) in any of the untreated strain backgrounds as shown in the representative images from Wild type (WT, BY4741) and dpl1Δ (YKB3306) backgrounds. (E) PC(O-16:0/2:0) treatment disrupts ceramide metabolism. Wild type (WT, BY4741) and dpl1Δ strains were treated with vehicle or PC(O-16:0/2:0) (20 μM) for the indicated times (min). Lipids were extracted and levels were quantified and expressed as a log2 fold change of PC(O-16:0/2:0) treated from vehicle treated isogenic control. LCB, long chain base; LCBP, long chain base phosphate (F)The hyperactive allele of the TORC2 target Ypk1 prevents ROS production. Wild type (BY4741) cells expressing empty vector (Vector, pRS416), wild type Ypk1 (Ypk1WT) or hyperactive Ypk1D242A (Ypk1D242A) were grown to mid log, treated with PC(O-16:0/2:0) (20 μM, 15 min) and labeled with H2-DCFDA (10 μM). Quantification for all experiments represents the average percentage of positive cells from at least three independent experiments where a minimum of 150 cells were counted. Error bars = SEM. (*p < 0.05 Kruskal-Wallis). ND – not detected. (G) Model of potential mechanism by which PC(O-16:0/2:0) inhibits TORC2/Ypk1 signaling via the ceramide/LCBP rheostat. Elevated concentrations of PC(O-16:0/2:0) promote an increase in ceramide levels which are associated with PES formation and inhibition TORC2-dependent Ypk1 phosphorylation leading to impaired mitochondrial function and increased production of ROS.