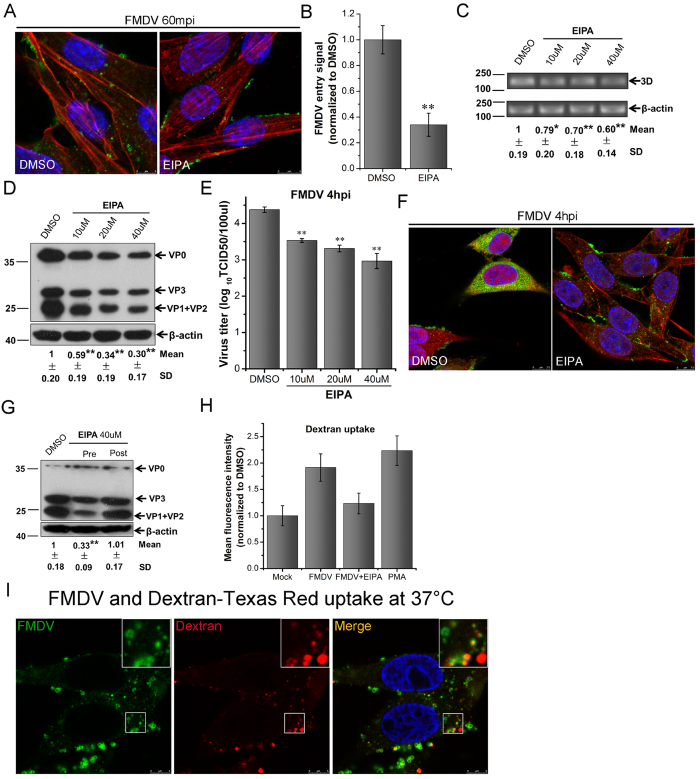
Figure 5. EIPA inhibits FMDV entry into BHK-21 cells and FMDV stimulates fluid-phase uptake.
(A) EIPA inhibited FMDV entry. Pretreated cells (40 μM EIPA) were infected (MOI 25) for 1 h at 37 °C and then processed for confocal microscopy with AF594-phalloidin (red), anti-FMDV (green), and DAPI (blue). (B) Quantitative analysis of the internalization of FMDV. The internalized FMDV were analyzed in 10 individual DMSO- or EIPA-treated cells. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and the results were presented as the mean ± SD. (C–E) Pretreated cells (EIPA) were infected (MOI 1) for 4 h at 37 °C and analyzed by RT-PCR (C), Western blot (D), and TCID50 assay (E). (F) Pretreated cells (0.2 μM EIPA) were infected (MOI 25) for 4 h at 37 °C and processed for confocal microscopy as in (A). (G) Effect of EIPA on virus entry and post-entry steps. Cells were treated with EIPA 30 min before the infection (Pre) or treated 60 min after virus addition (Post) and maintained during the infection. Cells were then infected (MOI 1) for 4 h at 37 °C and processed for Western blot analysis. (H) FMDV stimulated fluid-phase uptake. Cells were pretreated (40 μM EIPA) and infected (MOI 10) or stimulated with PMA for 30 min, pulsed with AF594-dextran for 15 min, and analyzed by FACS. (I) FMDV colocalized with dextran. FMDV (MOI 25) was allowed to bind to cells for 1 h at 4 °C. The inoculum was replaced with medium containing AF594-dextran and incubated for 15 min in 37 °C. Cells were fixed and incubated with anti-FMDV antibody (green). 3D, FMDV 3D; β-actin, load control; SD, standard deviation; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.