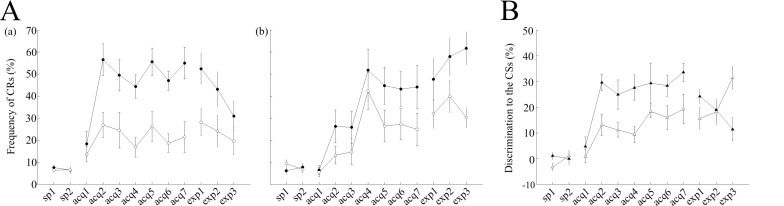
Fig 2. Effects of scopolamine on the acquisition and expression of the conditioned response (CR).
After 2 days of adaptation sessions (sp1–2), both saline–and scopolamine–treated mice underwent acquisition sessions for 7 consecutive days (acq1–7) followed by 3 days of expression sessions (exp1–3). (A) The left and middle panels represent the averaged CR frequency in both cued and non-cued trials. (a) Averaged data from cued trials (filled circles; n = 8) and non-cued trials (empty circles; n = 8) are illustrated for saline-injected control mice. (b) Averaged data from cued trials (filled circles; n = 8) and non-cued trials (empty circles; n = 8) are shown for scopolamine-injected mice. (B) The right panel represents the discrimination (%) to the CSs between the groups. Differences in discrimination percentage between cued and non-cued trials are plotted for the saline-treated (filled triangles) and scopolamine–treated mice (empty triangles). In panel A, the vertical axis represents the CR(%) frequency while the horizontal axis illustrates corresponding sessions and the vertical bars indicate the standard error of the mean. In panel B, the vertical axis represents discrimination to the CSs(%), while the horizontal axis illustrates corresponding sessions and the vertical bars indicate the standard error of the mean. sp, spontaneous session; acq, acquisition session; exp, expression session.