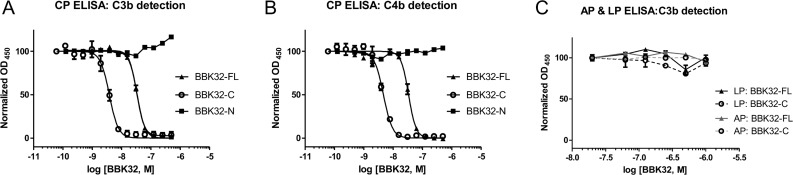
Fig 3. The C-terminal domain of BBK32 specifically inhibits the CP in a dose-dependent manner in an ELISA based assay of complement function.
CP was selectively activated by immobilization of human IgM followed by incubation of 1% human serum in GHB++ buffer in the presence of varying concentrations of BBK32 proteins. Monoclonal antibodies were used to detect the deposition of the complement activation products (A) C3b or (B) C4b. While BBK32-FL and the BBK32-C potently inhibit the CP in a dose-dependent manner, BBK32-N showed no apparent inhibitory activity. In contrast, when conditions were used to select for (C) AP activation (LPS coating, 20% serum, GHB°, Mg-EGTA) or LP activation (mannan coating, 1% serum, GHB++) no significant inhibition was detected for up to 1 μM concentrations of any BBK32 protein derivative. Wells containing serum only or where serum was replaced with buffer were treated as 100% and 0% signal, respectively. All experiments were performed a minimum of three times, errors are reported as the mean ± SEM, and calculated IC50 values are reported in Table 2.