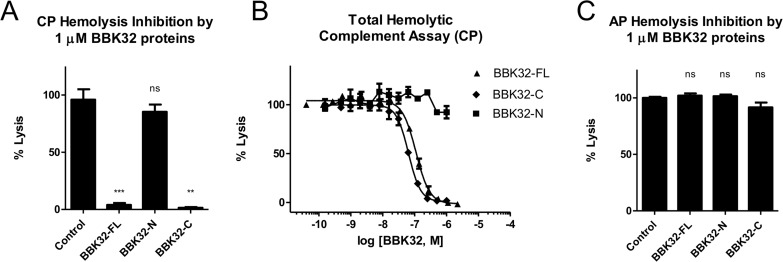
Fig 4. The C-terminal domain of BBK32 specifically inhibits CP-mediated hemolysis.
(A) The effect of 1 μM BBK32 proteins on CP-mediated hemolysis was assessed using a standard assay of complement hemolytic function (CP50). (B) While BBK32-N exhibited no measurable effect, BBK32-FL and BBK32-C abrogated nearly all hemolytic activity in a dose-dependent manner. (C) In contrast, BBK32 proteins fail to inhibit AP-mediated hemolysis. Measures of statistical significance in (A) and (C) were determined by use of an unpaired t test of each experimental series versus buffer control. ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001; ns, not significant. All experiments were performed between two and four times and errors are reported as the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM). Calculated IC50 values for the dose-dependent inhibition of CP hemolysis are reported in Table 2.