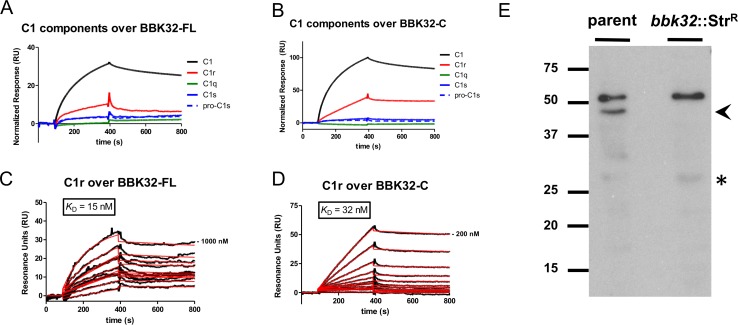
Fig 5. BBK32 forms a calcium-dependent, high-affinity interaction with the C1 subunit, complement C1r.
SPR analysis was used to evaluate C1 component binding to BBK32-FL or BBK32-C. C1 or individual protein constituents of the C1 complex were injected at a fixed 50 nM concentration over the surface of immobilized (A) full-length BBK32-FL or (B) BBK32-C. As SPR signal is directly proportional to molecular weight, the resulting sensorgrams were normalized using the molecular weight of each analyte species. Only injection of C1 or C1r enzyme resulted in significant binding. The SPR response (black lines) was recorded for a twofold dilution injection series of C1r enzyme in a running buffer of HBS-T-Ca2+ over immobilized (C) BBK32-FL or (D) BBK32-C. Five independent injection series were collected and sensorgrams shown are from a representative experiment. Red traces represent fits from kinetic evaluation of the injection series. The derived binding constants and fitting statistics are reported in Table 1. (E) Far Western Blot analysis was used to assess interaction of B. burgdorferi lysates with C1r enzyme. Biotinylated C1r enzyme was used to probe cell lysates from B. burgdorferi B31 strain ML23 grown under conventional (pH 7.6) conditions. Proteins of apparent molecular weights 28, and 48, and 54 kDa were capable of binding C1r in the parent strain, while the 48-kDa band alone was absent from the strain lacking an intact bbk32 locus (bbk32::StrR). An arrowhead denotes the band corresponding to BBK32 while an asterisk denotes a band migrating to a position observed in the C1 Far Western (Fig 1A).