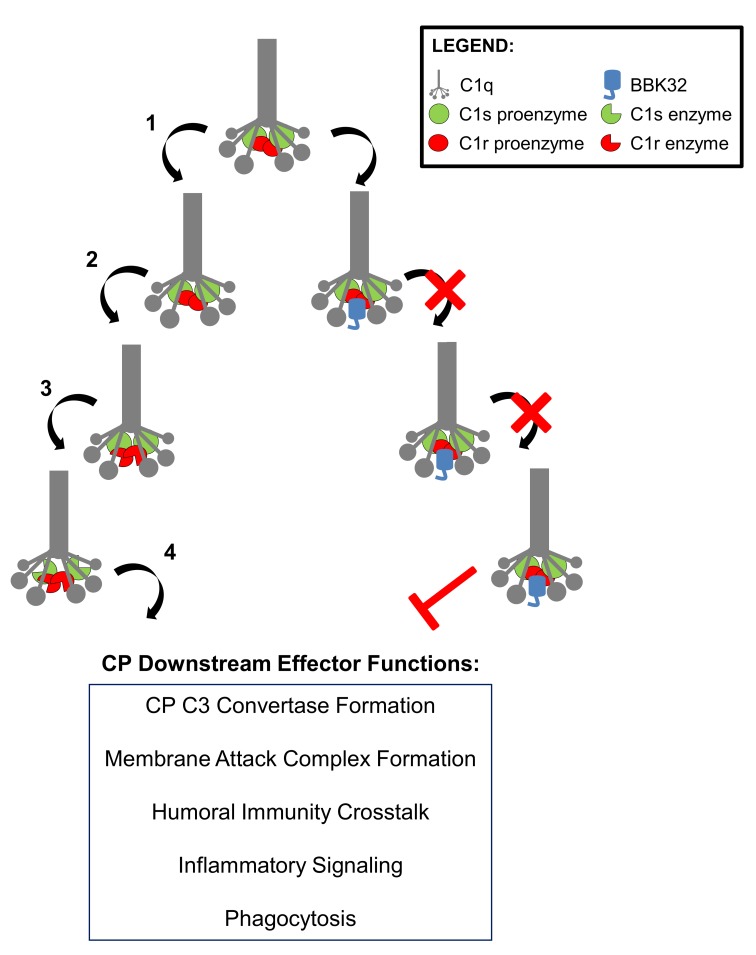
Fig 10. Model of C1 inactivation and CP inhibition by BBK32.
C1 circulates as an inactive zymogen composed of one C1q molecule, two C1r proenzyme molecules, and two C1s proenzyme molecules. The pathway on the left depicts the normal uninhibited activation of C1 that proceeds by binding of the pattern recognition molecule C1q to a bacterial surface (1). C1q binding triggers the autocatalysis of the C1r proenzymes (2) that subsequently cleave and activate C1s (3). C1s then cleaves downstream CP components (4), which ultimately lead to many downstream CP effector functions. The pathway on the right side depicts the situation in the presence of the BBK32 lipoprotein. Following C1q binding to the borrelial surface the C-terminal domain of BBK32 recognizes C1 by binding directly to C1r. BBK32 blocks the autocatalytic and C1s proenzyme proteolysis functions of C1r (denoted in both instances by a red X). Thus, BBK32 effectively renders C1 in the zymogen form leading to abrogation of CP activation (denoted by a red bar).