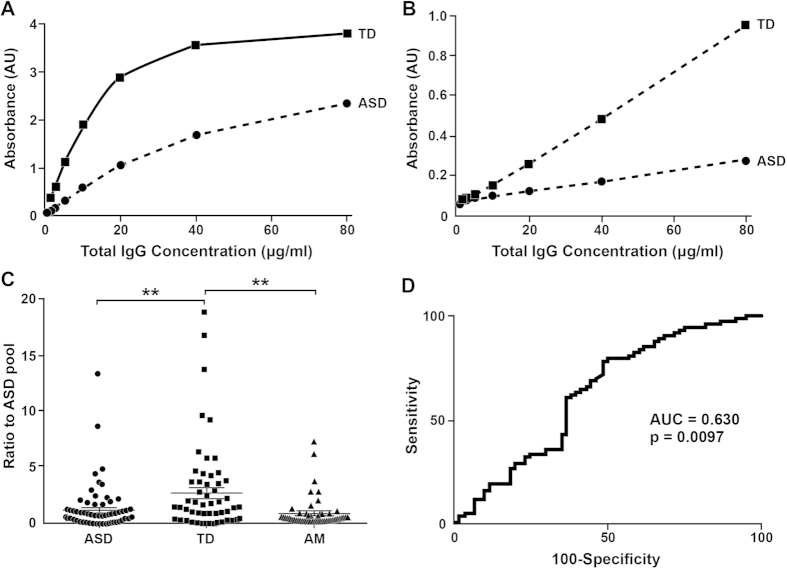
Figure 3. Serum IgG binding to the ASD1 peptoid.
(A) Titration of IgG binding to ASD1 using serum pooled from 10 TD males and 10 ASD males demonstrates ASD1’s ability to differentiate between the two groups. (B) Detecting IgG1 subclass instead of total IgG amplifies this differentiation. (C) IgG1 binding of individual ASD (n=74) and TD (n=60) male serum samples (1:100 dilution) to ASD1 significantly differs with TD>ASD. In addition, IgG1 binding of older adult male (AM) serum samples (n=53) to ASD1 is significantly lower than TD males, and not different from ASD males. The three groups were compared with a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, H = 10.1781, p<0.006. **p<0.005. Error bars show SEM. (D) Receiver-operating characteristic curve for ASD1’s ability to discriminate between ASD and TD males.