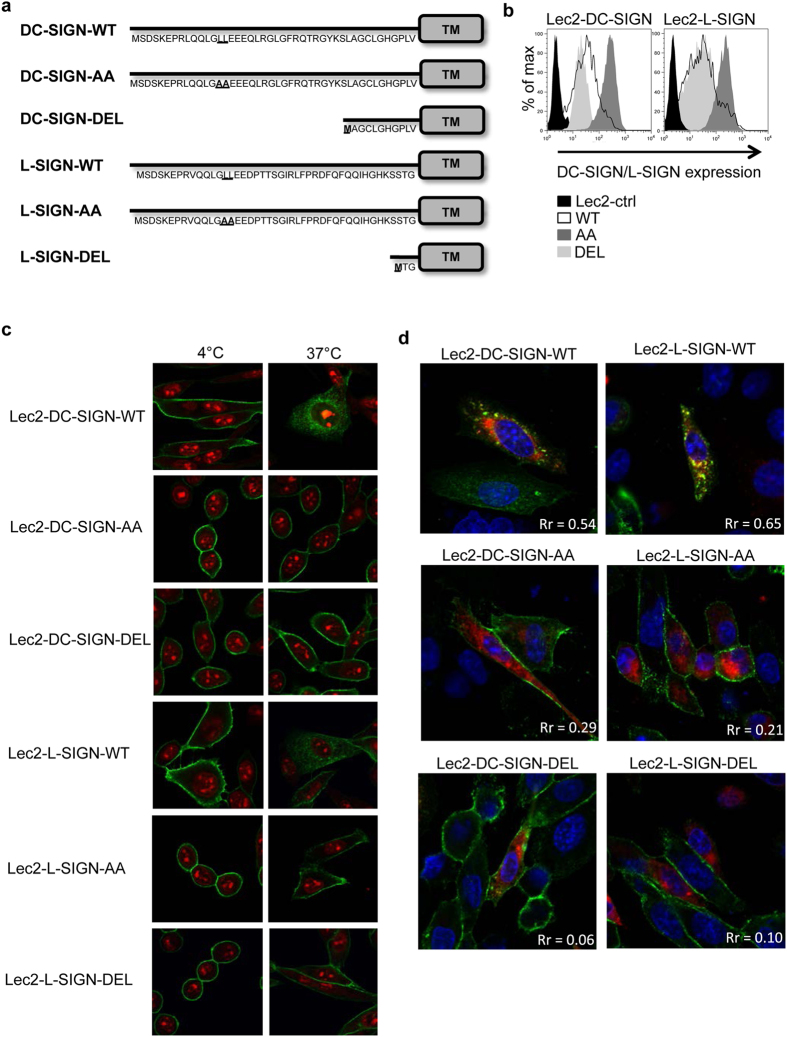
Figure 2. Generation and characterisation of cells expressing WT, AA or DEL mutants of DC-SIGN and L-SIGN.
(a) Schematic overview of the CLR mutants. The amino acid sequence of the cytoplasmic domain of wild-type (WT) DC-SIGN and L-SIGN are shown, as well as mutants containing LL→AA mutations (AA) and deletion mutants lacking the entire cytoplasmic tail (DEL). Mutated residues are highlighted in bold and the transmembrane domain (TM) is shown. (b) FACS histograms showing cell-surface expression of DC-SIGN/L-SIGN on Lec2 cells expressing -WT, -AA or -DEL forms of the receptors. Lec2-ctrl cells were included for comparison. (c) Endocytic capacity of Lec2 cells expressing different forms of DC-SIGN/L-SIGN following cross-linking with antibody. Cell monolayers expressing -WT, -AA or -DEL forms of DC-SIGN/L-SIGN were incubated with anti-DC-SIGN/L-SIGN mAb for 1 hr at 4 °C, washed and incubated for a further 40 min either at 4 °C or 37 °C. Cells were then fixed and stained with Alexa Fluor-488 anti-mouse Ig (green, to detect anti-DC-SIGN/L-SIGN mAb) and propidium iodide (red, to stain the nucleus) and examined by confocal microscopy. (d) Cell monolayers were transiently transfected with a RFP-tagged Rab5 construct (red) and, 16 hr post-transfection, incubated with anti-DC-SIGN/L-SIGN mAb for 1 hr at 4 °C. After washing, cells were incubated at 4 °C or 37 °C for 40 min, and then fixed and stained with Alexa Fluor-488 anti-mouse Ig (green, to detect anti-DC-SIGN/L-SIGN mAb) and with DAPI (blue, to stain the nucleus). Co-localisation of Rab5 and DC-SIGN/L-SIGN was examined by confocal microscopy, where yellow staining is indicative of co-localisation.