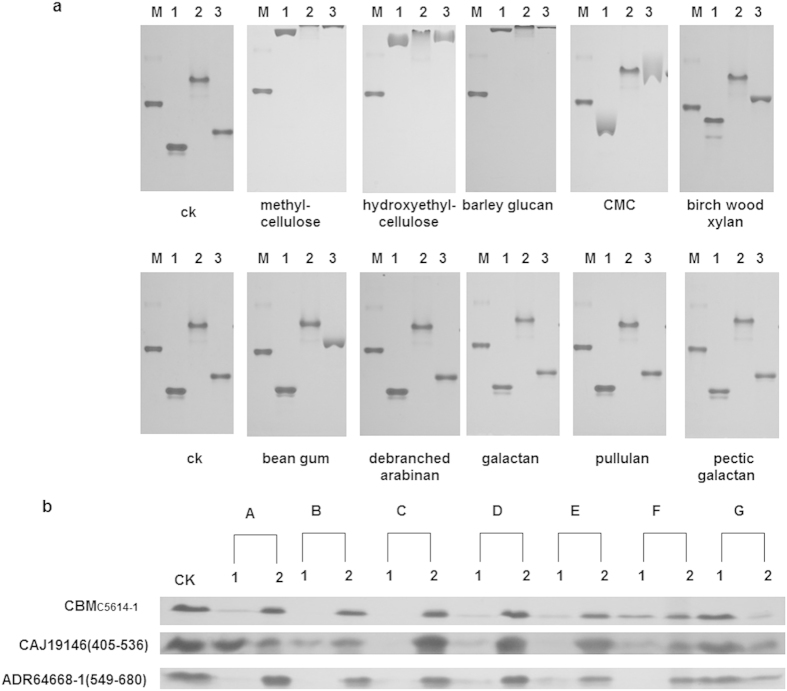
Figure 2. Binding of CBMC5614-1 and its homologs to polysaccharides.
(a) Binding of CBMC5614-1 and its homologs to soluble polysaccharides. Proteins and BSA were separated using non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels containing 0.1% (wt/vol) soluble polysaccharides. A gel without polysaccharides (CK) served as a control. M: BSA control (no polysaccharides bound); 1: CBMC5614-1; 2: CAJ19146 (405–536); 3: ADR64668-1 (549–680). (b) Binding of CBMC5614-1 and its homologs to insoluble polysaccharides. 30 μg of purified CBMC5614-1 and its homologs were incubated with 200 μl 4% (wt/vol) insoluble polysaccharide including Avicel (A), ASC (B), insoluble birch wood xylan (C), mannan (D), lichenan (E), raw starch from cassava (F) or agarose (G). The same amount of protein used in the binding assay but without polysaccharide was included as a control (CK). After centrifugation, unbound protein in the supernatant (lane 1) and bound proteins in the precipitate (lane 2) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE.