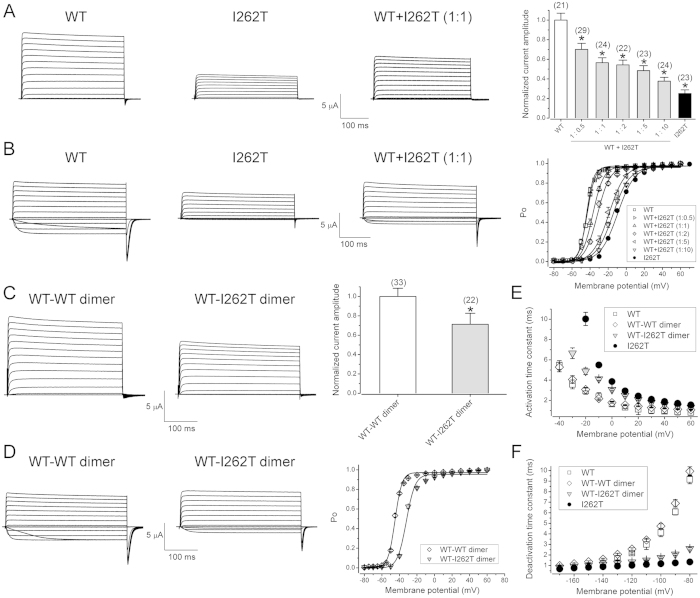
Figure 1. I262T exerts dominant effects on functional expression and voltage-dependent gating of Kv1.1 channels.
Functional characterization of the I262T mutant in Xenopus oocytes. (A) Dominant-negative effects of I262T. (Left) Representative current traces of Kv1.1 WT, I262T, and equal-molar co-expression of WT and I262T [WT + I262T (1:1)]. In all oocyte injection conditions hereafter, the cRNA concentration is 0.5 μg/μl for each construct. The external bath solution contains 3 mM KCl. The holding potential is −90 mV. The voltage protocol comprises a 370-ms test potential (ranging from −80 mV to + 60 mV in + 10 mV steps) followed by −90-mV tail potential. (Right) Normalized peak current amplitudes at the + 60-mV test potential. In the co-expression group (WT + I262T), the molar ratio of the mutant was increased from 0.5 up to 10. Data were normalized with respect to the average values of Kv1.1 WT recorded from the same batch of oocytes on the same day. Asterisks denote a significant difference from the WT control (*, t-test: p < 0.05). (B) I262T shifts the voltage-dependence of Kv1.1. (Left) Representative current traces in the external solution containing 60 mM KCl. (Right) Steady-state activation (Po–V) curves derived from isochronal tail currents at −90 mV in response to various test pulse potentials. (C) Representative current traces in 3-mM KCl bath solution (left) and normalized peak current amplitudes (right) of Kv1.1 WT-WT dimer and WT-I262T dimer. Asterisks denote a significant difference from the WT-WT dimer control (*, t-test: p < 0.05). (D) Representative current traces in 60-mM KCl bath solution (left) and Po–V curves (right) of WT-WT and WT-I262T dimers. (E,F) I262T slows activation kinetics but speeds deactivation kinetics of Kv1.1 channels. Activation and deactivation time constants were derived from one-exponential fits of the rising phase of test currents (3 mM KCl) and tail currents (60 mM KCl), respectively. See Supplementary Table S1 for more details on Po–V parameters.