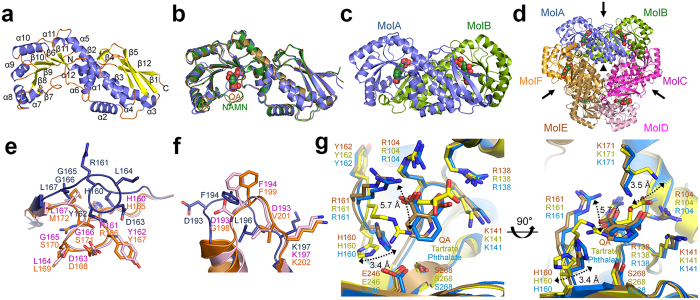
Figure 1. Overall structure and comparison of HsQPRT.
(a) Monomeric structure of HsQPRT. The 12 α-helices and 12 β-sheets represent α1–α12 and β1–β12, respectively. (b) Superimposition of the overall structures of monomeric HsQPRT in the apo form (blue), HsQPRT-QA (brown) and HsQPRT-NAMN (green). (c) Dimeric structure of HsQPRT. Substrate molecules (NAMN) are shown as spheres. (d) Hexameric structure of HsQPRT indicated a trimer of dimers (MolA-MolB, MolC-MolD and MolE-MolF). The two- and three-fold axes of the hexamer are indicated as arrows and triangles, respectively. (e,f) Structural comparison among HsQPRTs in HsQPRT-open (blue), HsQPRT-closed (magenta) and yeast apo enzyme (orange) in loop L (e) and loop O (f). (g) Structural comparison of HsQPRT in complex with QA (brown), tartrate (yellow) and phthalate (blue). Conformational changes are shown as two-sided arrows.