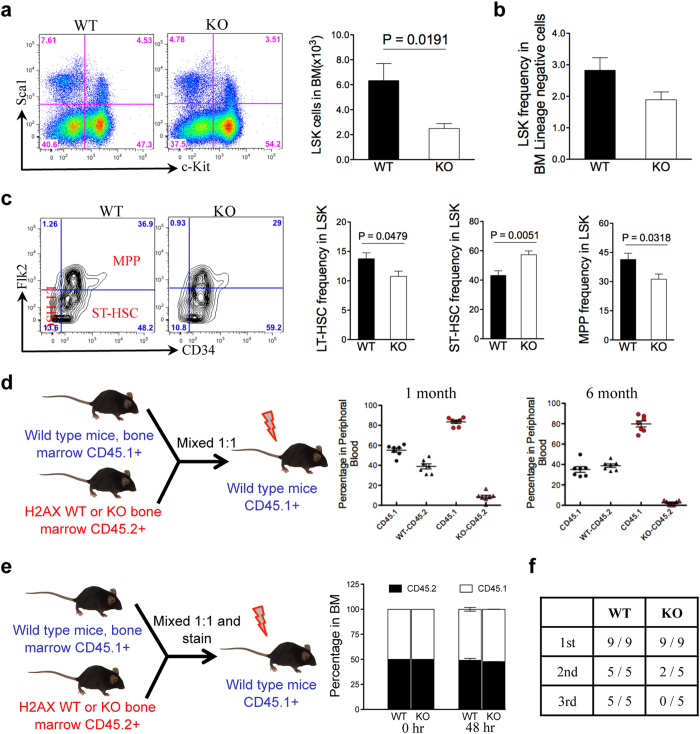
Figure 5. H2AX deficiency impairs HSC/progenitor function.
(a) Quantification of HSCs/progenitors. Lineage-negative bone marrow cells from 3-month-old H2AX knockout and wild-type mice were isolated and analysed by flow cytometry for the indicated surface markers (n = 5 per group). Quantification of the number of LSK cells is shown to the right. (b) Quantification of the percentage of LSK cells (n = 5 per group). (c) Representative flow cytometric profiles of long-term HSCs (LT-HSCs), short-term HSCs (ST-HSCs), and multipotent progenitors (MPPs) from pre-gated LSK cells in (a). Quantification of the indicated populations is shown to the right. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (d) Schematic illustration of the competitive transplantation assay. Bone marrow from 3-month-old H2AX knockout and wild-type mice (CD45.2-positive) was harvested and mixed with wild-type bone marrow (CD45.1-positive) at a 1:1 ratio and transplanted into lethally irradiated wild-type mice (CD45.1-positive, n = 8 per group). Quantification of donor chimerism in peripheral blood 1 and 6 months post-transplantation is shown to the right. (e) Schematic illustration of the homing assay. Bone marrow cells were harvested and mixed as in (d). The mixed bone marrow cells were stained in vitro and transplanted into lethally irradiated wild type mice (CD45.1-positive, n = 8 per group). Quantification of donor chimerism in bone marrow 48 hours post-transplantation is shown to the right. (f) Noncompetitive serial transplants were initiated by transplanting 2 × 106 bone marrow cells from 3-month-old H2AX knockout and wild-type mice (CD45.2-positive) into lethally irradiated recipient mice (CD45.1-positive, n = 8 per group). Secondary and tertiary transplants were performed 4 months later (n = 9 per group in the first transplantation, n = 5 per group in the secondary and tertiary transplantations). Numerator indicates the number of surviving mice.