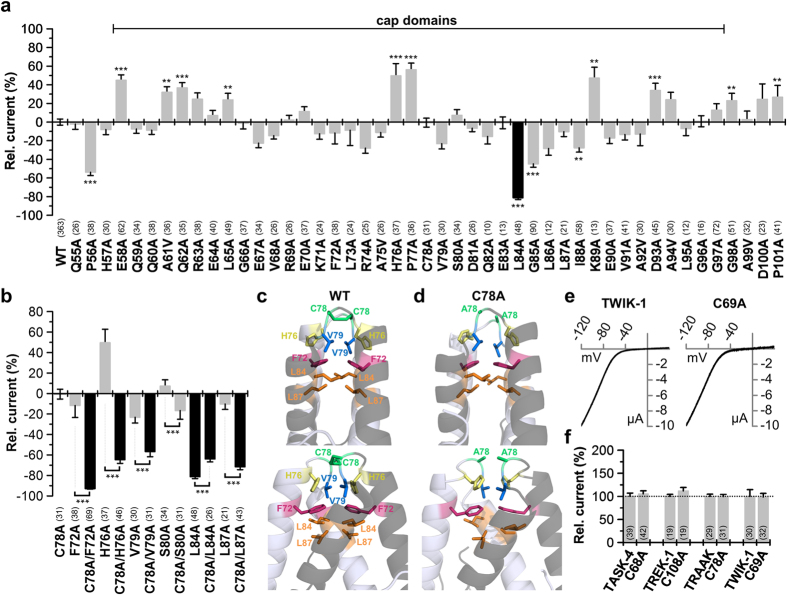
Figure 7. Alanine scan through the extracellular M1-P1 linker of human TRAAK.
(a) Relative current amplitudes at +40 mV compared to TRAAK wild-type (WT). Mutations in the cap exhibiting a pronounced current amplitude reduction are highlighted in black. Note that the C78A mutation at the tip of the cap structure did not affect current amplitudes. (b) TRAAK mutations at the sites homologous to the TASK-1 ‘hits’ were functionally studied in TRAAK alone (as in (a)) or in the absence of the cysteine at position 78 (C78A). F72 in TRAAK corresponds to L48 in TASK-1, H76 to Y52, C78 to N53, V79 to L54, S80 to S55, L84 to Y59 and L87 to L62. Pronounced reduction in current amplitudes compared to the C78A mutant alone are illustrated in black. (c) Domain-swapped TRAAK cap structure after 10 ns of MD simulation illustrating the relevant residues identified in (b). Upper panel shows the orientation as in Brohawn et al., 2012 and the lower panel is rotated by 90°. (d) Domain-swapped TRAAK cap structure of the C78A mutation after 10 ns of MD simulation, illustrating the relevant residues identified in (b). Upper panel shows the orientation as in Brohawn et al., 2012 and the lower panel is rotated by 90°. (e) Representative current traces of TWIK-1 and TWIK-1 C69A recorded in oocytes, using a voltage ramp from −120 to +40 mV. (f) Changes in relative current amplitudes at +40 mV, after mutating the conserved cysteine residues in the cap structure of different K2P channels. (a,b,f) **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Significance was probed using unpaired Student’s T-Test against the respective wild-type channel, unless for panel (b), here significance of the double mutation was probed against the respective single mutation without C78A. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. The number of experiments are given above the construct name or included in the bar graphs.