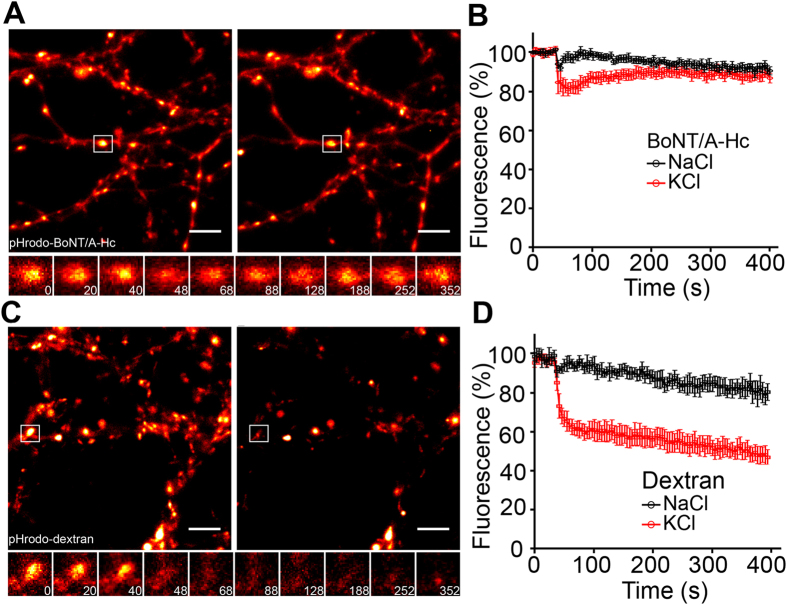
Figure 4. BoNT/A-Hc-containing vesicles exhibit reduced ability to undergo exocytosis at the presynaptic nerve terminal of hippocampal neurons.
Hippocampal neurons (14–17 days in vitro) were loaded with either pHrodo-BoNT/A-Hc (300 nM) (A,B) or pHrodo-dextran (0.1 mg/ml) (C,D) during a 2 min high K+ stimulation. Neurons were left to recover for 12–15 min prior to a second stimulus (30 mM KCl or NaCl as control) during which a time-lapse movie was acquired. (A,C) Representative nerve terminals prior to the second KCl stimulus and (B,D) 400 s following the stimulus. Enlargements show the response of a representative nerve terminal to the second stimulation over time. Scale 5 μm. (E,F) Normalized fluorescence of nerve terminals loaded with pHrodo-BoNT/A-Hc (n = 8 experiments from 2 independent preparations) (E) or pHrodo-dextran (n = 4 experiments from 2 independent preparations) (F) in response to a KCl stimulation or NaCl control. Data are plotted as mean ± sem.