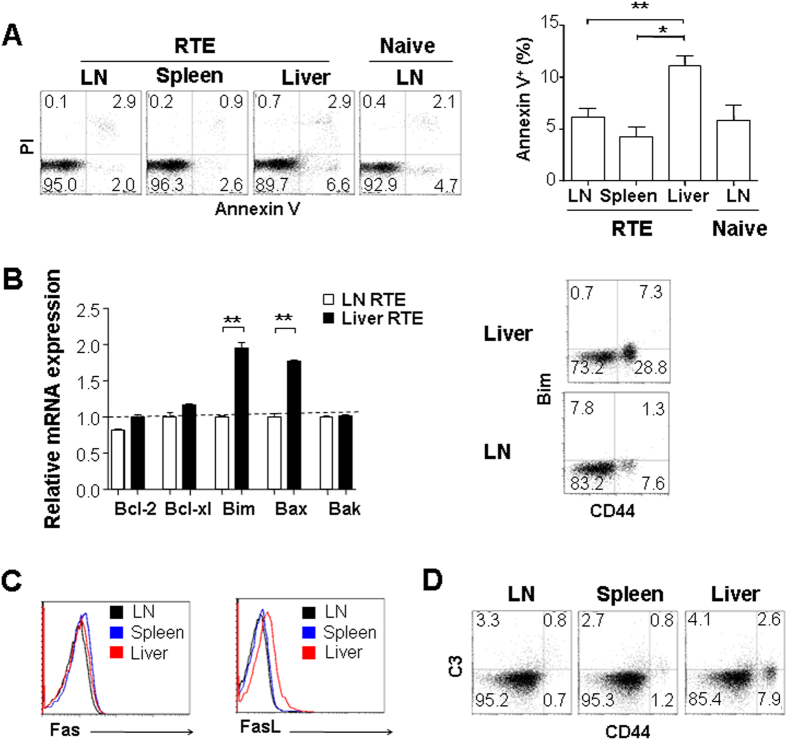
Figure 2. The apoptosis of liver persisting CD4+ RTEs.
(A) RTEs in the liver undergo more apoptosis than those in other lymphoid tissues. GFP+ CD4+ CD8− CD25- RTEs from mesenteric lymph nodes (LN), spleen, and liver of RAG2p-GFP transgenic mice were stained with Annexin V and Propidium iodide (PI) and analyzed by flow cytometry. The average percentages of annexin V+ cells were plotted and the statistical significance between any two tissues was calculated by Student t-test. (B) CD4+ RTEs in the liver express higher level of pro-apoptotic molecules Bim and Bax when compared to RTEs in LN. Total RNA was extracted from CD4+ RTEs purified from LNs and liver and quantitative RT-PCR was performed to compare the transcription of Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Bim, Bax, and Bak (left panel). The comparison of Bim protein level by flow cytometry was also performed in liver and LN RTEs (right panel). (C) Expression of FasL, but not Fas in CD4+ RTEs is higher in the liver than in LNs and spleen. (D) Similar levels of complement C3 deposition on the surface of CD4+ RTEs obtained from the liver, LN, and spleen. Two or three independent experiments were performed and similar results were obtained.