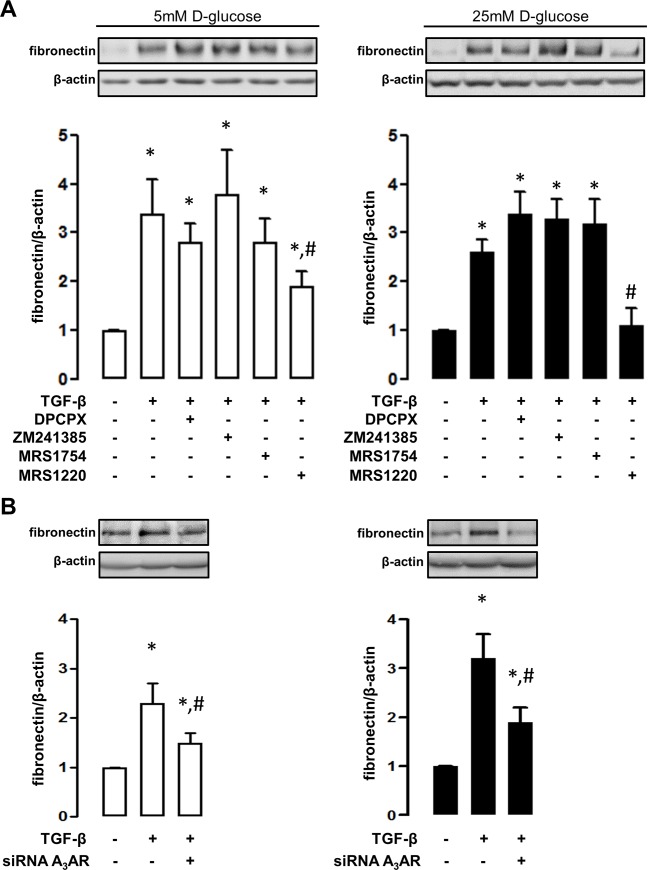
Fig 5. An antagonist of adenosine A3 receptor blocks profibrotic activation induced by TGF-β.
A. The induction of the marker fibronectin was evaluated by western blots in HK2 cells upon exposure to TGF-β. The contribution of a particular adenosine receptor subtype in TGF-β-induced cell activation, was recognized by using selective pharmacological antagonists. Selective antagonists were DPCPX (30nM) for A1, ZM241385 (10nM) for A2A, MRS1754 (50nM) for A2B and MRS1220 for A3 (10nM) receptor subtypes. B. The particular contribution of the adenosine A3 receptor was evidenced by knocking down the expression of the receptor using siRNA (siRNA A3AR). The upper images show representative western blot detections of fibronectin content in total protein extracts (50 μg) from treated HK2 cells. The blocking effect was assayed in HK2 cells cultures 5mM (left white bars graphs) or 25mM (right black bars graphs) D-glucose. The graphs represent the mean ± SD of the ratio between immune signals of fibronectin vs β-actin. The ratio in HK2 cells without TGF-β treatment was normalized to 1. * P < 0.05 versus untreated cells, # P < 0.05 versus TGF-β, n = 5.