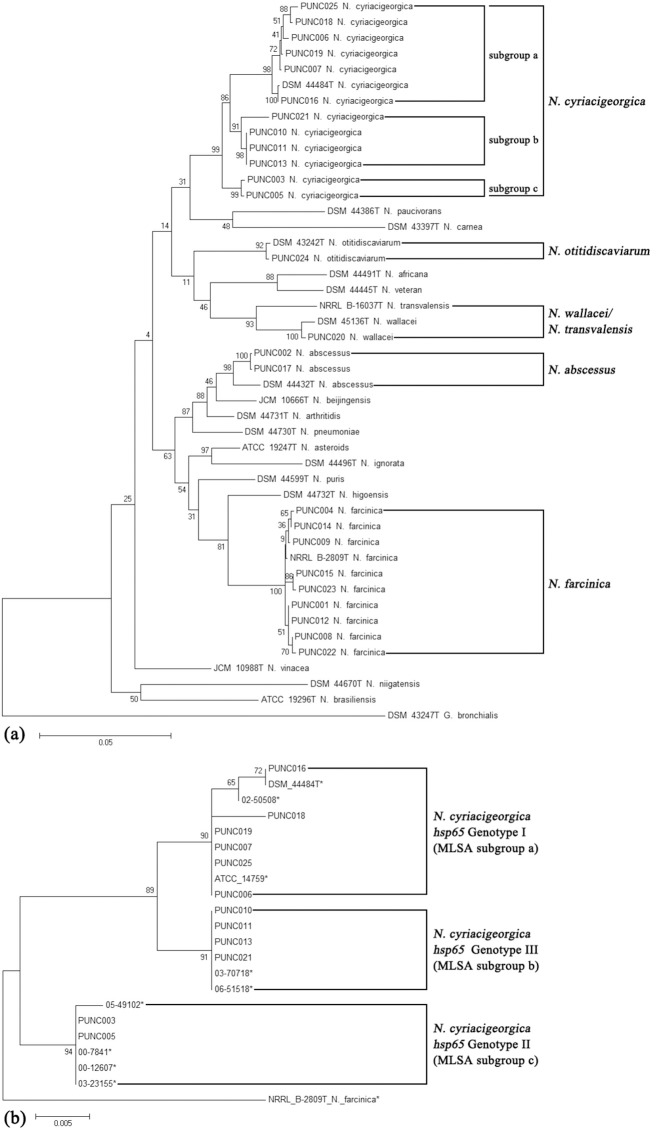
Fig 1. Phylogenetic trees are shown and were conducted using the maximum-likelihood method.
Fig 1a. Phylogenetic tree based on the concatenated gyrB-16S-secA1-hsp65-rpoB sequences of 25 Nocardia clinical isolates and 20 Nocardia type strains, using Gordonia bronchialis strain ATCC 25592T as an outgroup (S1 Table). Fig 1b. Phylogenetic tree based on the hsp65 gene sequences of 12 N. cyriacigeorgica clinical isolates and nine Nocardia cyriacigeorgica isolates whose genotypes have previously been determined by Schlaberg et al. [29] using the sequence of a Nocardia farcinica strain as an outgroup.