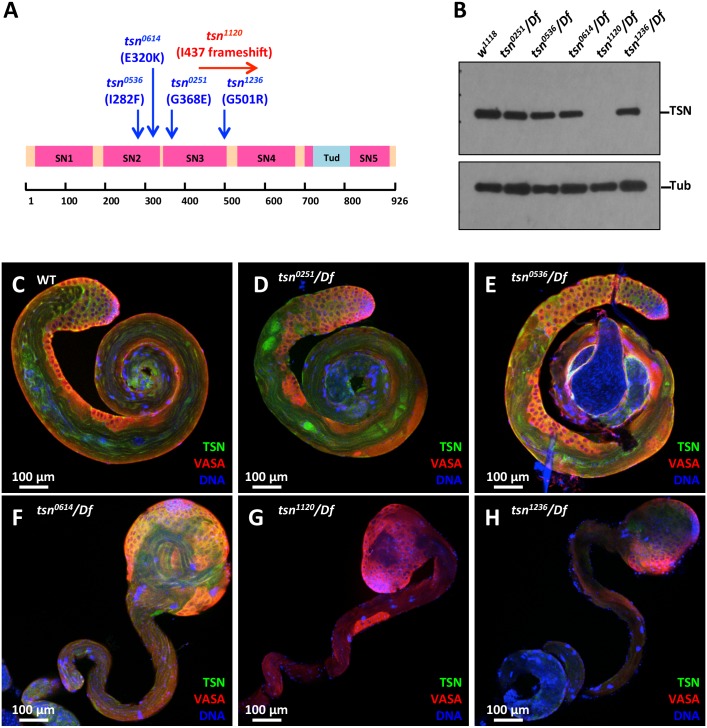
Fig 3. Mutations of tsn result in abnormal spermatogenesis.
(A) The EMS mutant alleles of tsn. The position of each mutation is indicated by an arrow above a schematic representation of the TSN protein. tsn0536 and tsn0614 are point mutations at 282Ile→Phe and 320Glu→Lys of the SN2 domain, respectively. tsn0251 and tsn1236 are point mutations at 368Gly→Glu and 501Gly→Arg of the SN3 domain, respectively. tsn1120 is a deletion mutation which causes frameshift from 437Ile of the SN3 domain. (B) TSN protein expression level in the adult testes of each mutant allele heterozygous with a deficiency (Df) that disrupts the TSN genomic locus was analyzed by Western blots. TSN was undetectable in the lysates from tsn1120/Df testes. (C-H) Immunostaining of TSN (using mouse anti-TSN antibody, green) and VASA (red) in the testes from the five tsn mutant alleles heterozygous with the Df allele. DNA was labeled by DAPI (blue). tsn0614/Df (F), tsn1120/Df (G), and tsn1236/Df (H) resulted in the swollen apical tip of the testis. TSN was barely detectable in the tsn1120/Df testis (G). tsn0251/Df (D) and tsn0536/Df (E) did not cause obvious testicular phenotype compared to the WT testis (C).