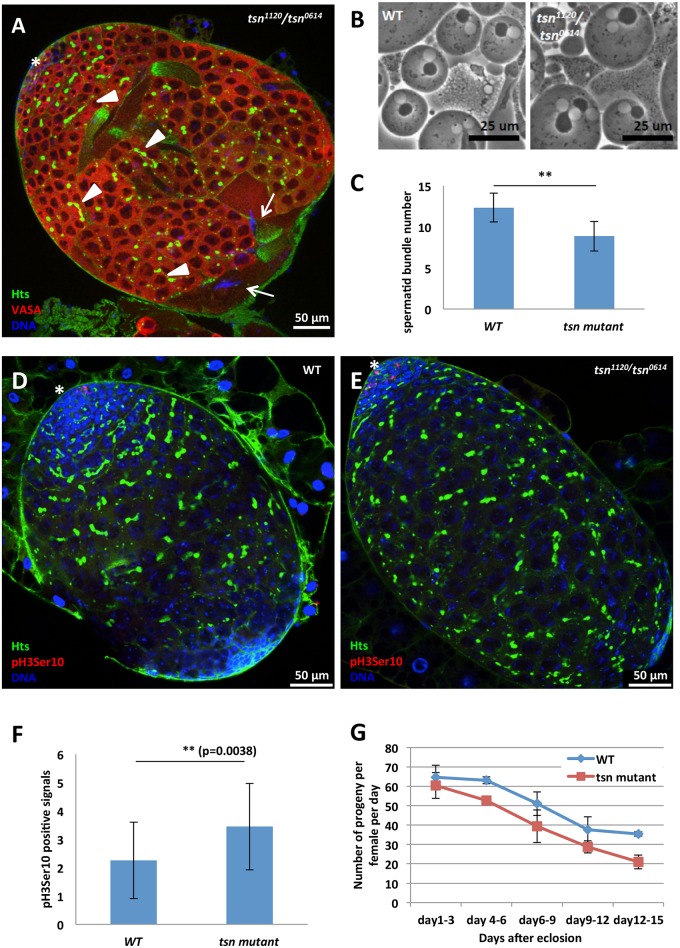
Fig 4. tsn mutations cause spermatogenic cell overproliferation, cytokinetic defects during meiosis, fewer spermatid bundles, and reduced male fertility.
(A) The apical tip region of 2-day-old adult tsn1120/tsn0614 mutant testes. Testes were stained with anti-VASA (germ cell, red) and anti-Hts (fusome, green) antibodies. DNA was labeled by DAPI (blue). The swollen apical tip of the mutant testis was filled with VASA-positive germ cells containing branched fusomes (arrow head) and faint DNA staining, indicating these cells are spermatocytes. A few bundles of elongated spermatids with their heads (arrow) resided at the apical tip of the mutant testis, in contrast to their normal localization at the basal region of the testis. Asterisk: the hub. (B) Phase contrast images of round spermatids from adult WT (left) and tsn1120/tsn0614 mutant (right) testes. In mutant testes, round spermatids containing a single Nebenkern (mitochondrial derivates) associated with two haploid nuclei were observed, indicating there were meiotic cytokinesis defects (see text). (C) The quantification of spermatid bundle number in 2-week-old adult testes revealed that tsn1120/tsn0614 mutants had fewer spermatid bundles compared to the WT. (D-E) The third instar larval testes of WT and tsn1120/tsn0614 mutant were immunostained with anti-phospho-histone3 (pH3, mitotic index, red) and anti-Hts (fusome, green) antibodies. DNA was labeled by DAPI (blue). Asterisks indicate the hubs. The tsn mutant testis had more pH3-positive spermatogonia and was larger in size. (F) The quantification of pH3-positive spermatogonia per testis. The WT testes showed an average of 2.56 pH3-positive cells per testis (n = 27) and the tsn1120/tsn0614 mutant had an average of 3.44 pH3-positive cells per testis (n = 27) (see text). (G) The fertility of tsn mutant (red line) and WT (blue line) males. Initially, the tsn1120/tsn0614 mutant males showed a similar fertility as the WT controls, but the fertility was decreased faster over time compared to the WT males. Error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean ((C) and (F) N ≧ 27; (G) N≧ 3). ** denotes P<0.01. The differences between WT and tsn mutant males In (G), p = 0.0000437 (by t-test) for the differences between WT and tsn mutant males.