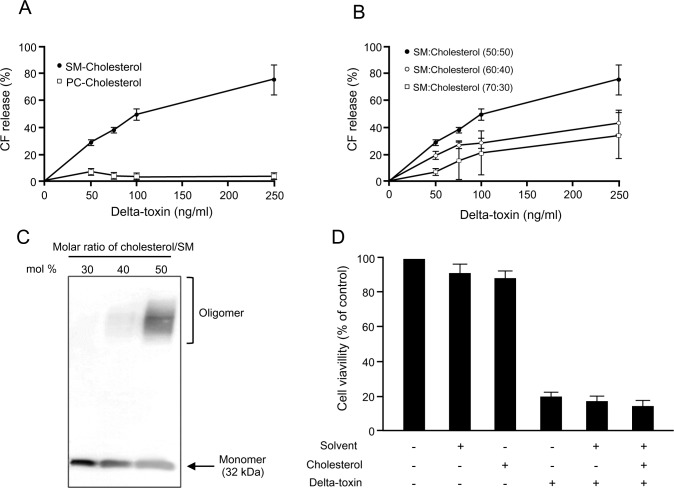
Fig 3. Delta-toxin induced carboxyfluorescein release from phospholipid-cholesterol liposomes.
(A) Carboxyfluorescein (CF)-loaded liposomes each composed of SM or PC and cholesterol at a molar ratio of 50:50 mol % were treated with delta-toxin for 30 min at 37°C. (B) Liposomes composed of sphingomyelin (SM) and cholesterol at several molar ratios were treated with delta-toxin for 30 min at 37°C. The molar ratio of cholesterol to SM (mol %) was 50, 40, or 30. CF release was measured as described in the Materials and Methods. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) of four experimental studies is shown. (C) Liposomes composed of SM and cholesterol at various molar ratios (50, 40 or 30 mol %) were treated with delta-toxin (1 μg/ml) for 30 min at 37°C. Liposome-bound toxin was solubilized and confirmed by immunoblotting of delta-toxin. The result is representative of four experimental studies. (D) Effect of cholesterol on cytotoxicity caused by delta-toxin. To assay cholesterol inhibition, a 50 μl volume of cholesterol in absolute ethanol was added to 1 ml aliquots of 50 ng/ml delta-toxin preparations, to a final concentration of 1 μg/ml. After 30 min treatment at room temperature, cytotoxicity was assayed as described in the Materials and Methods. Cell viability was assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)- 2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazilum (MTS) method. Results are indicated as percentage of the value for controls. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) for four experimental studies is shown.