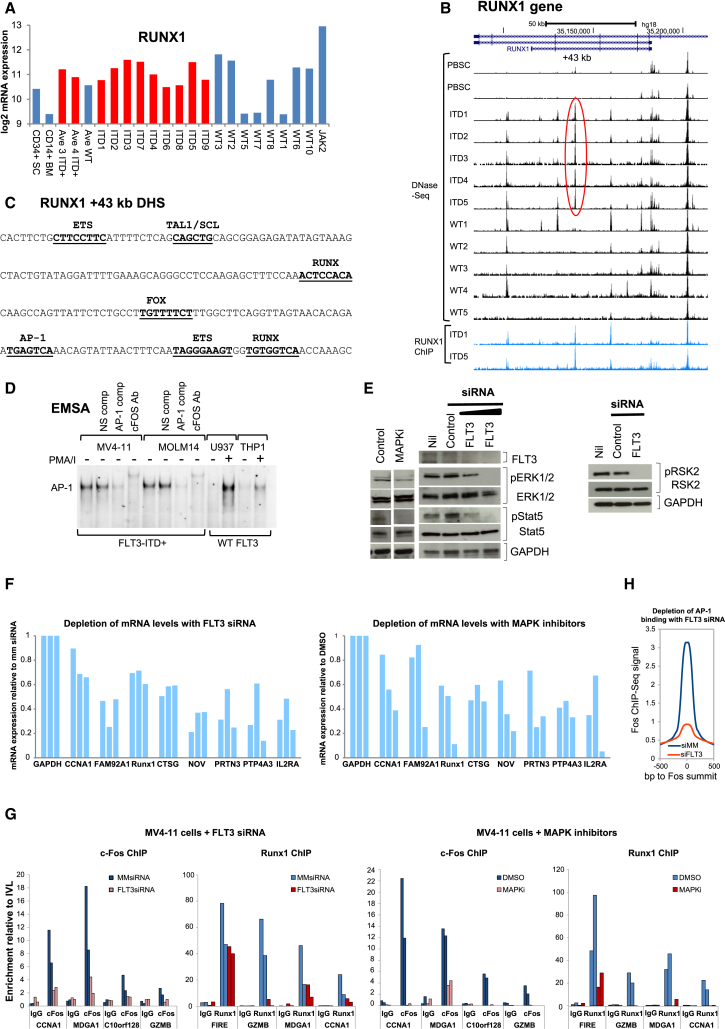
Figure 6.
AP-1 and RUNX Pathways Are Activated in ITD+ AML
(A) Log2 RUNX1 mRNA microarray values.
(B) UCSC Genome Browser view for RUNX1 DNase-seq.
(C) Sequence of the ITD-specific RUNX1 +43-kb DHS with the indicated sequence motifs underlined, which underlay the ITD-specific DHS signature.
(D) EMSA using nuclear extracts from the indicated cell lines grown in the presence and absence of stimulation for 2 hr with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and calcium ionophore A23187 (PMA/I) to induce AP-1 activity. Some assays include AP-1 or non-specific (NS) DNA competitors or FOS antibodies.
(E) Western blot analyses extracts from ITD+ MV4-11 cells treated with FLT3 or mismatch (MM) control siRNA, using the indicated antibodies.
(F) RT-QPCR analysis of ITD target gene mRNA expression after treatment of MV4-11 cells with either siRNA against FLT3 (left) or with the MAPK pathway inhibitors PD98059, SP600125, and SB202190 directed against MEK1/2, JNK, and p38, respectively (right), from three independent experiments for each gene. Values were calculated relative to GAPDH.
(G) ChIP analyses of FOS and RUNX1 binding to ITD-specific DHSs, with normal IgG used as a control. Data are expressed relative to FOS or RUNX1 binding to a region in the inactive IVL locus.
(H) Average FOS ChIP peak profiles obtained from MV4-11 cells treated with either FLT3 or MM siRNA.